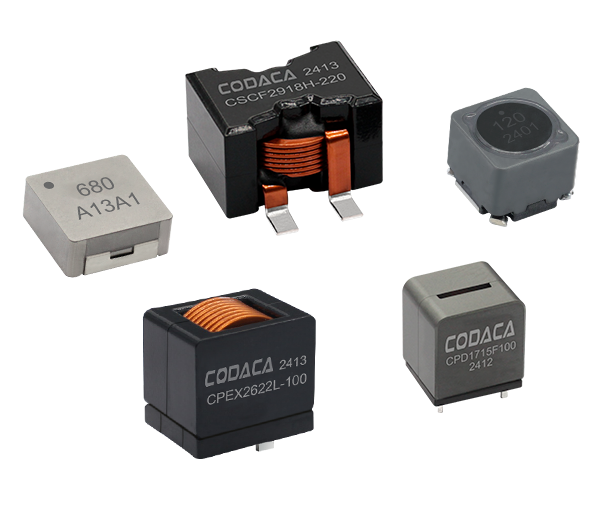
סליל ספק כבוי SMD
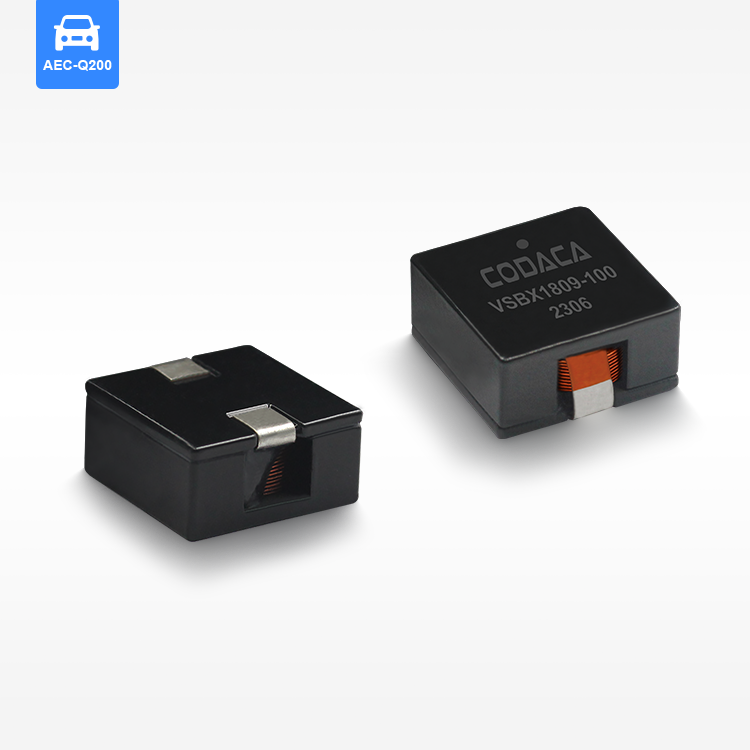
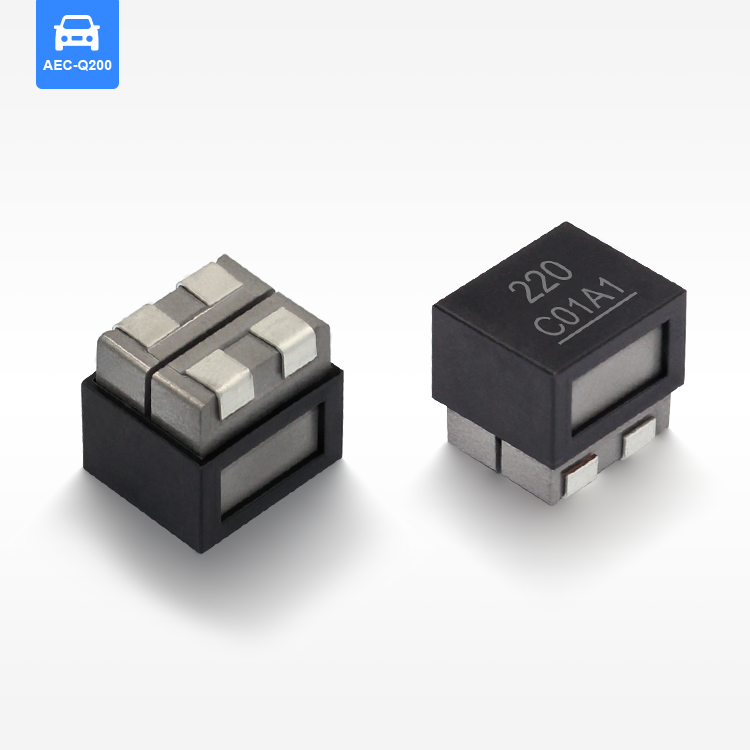
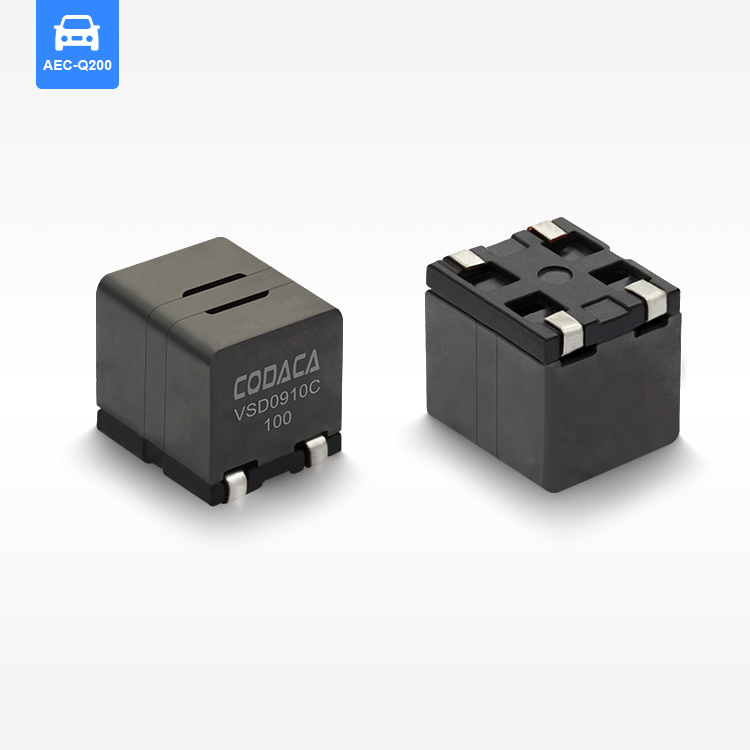
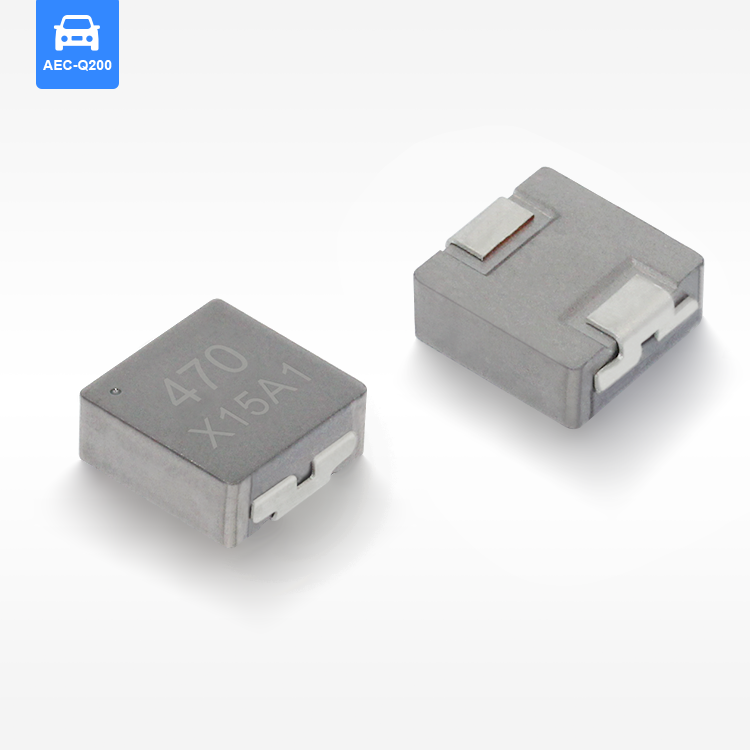
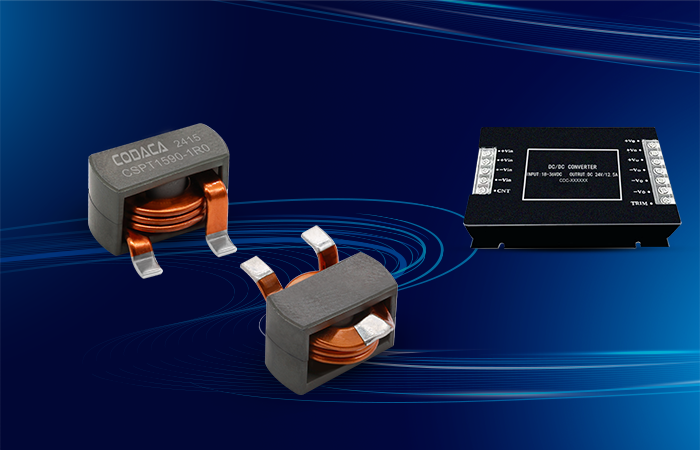
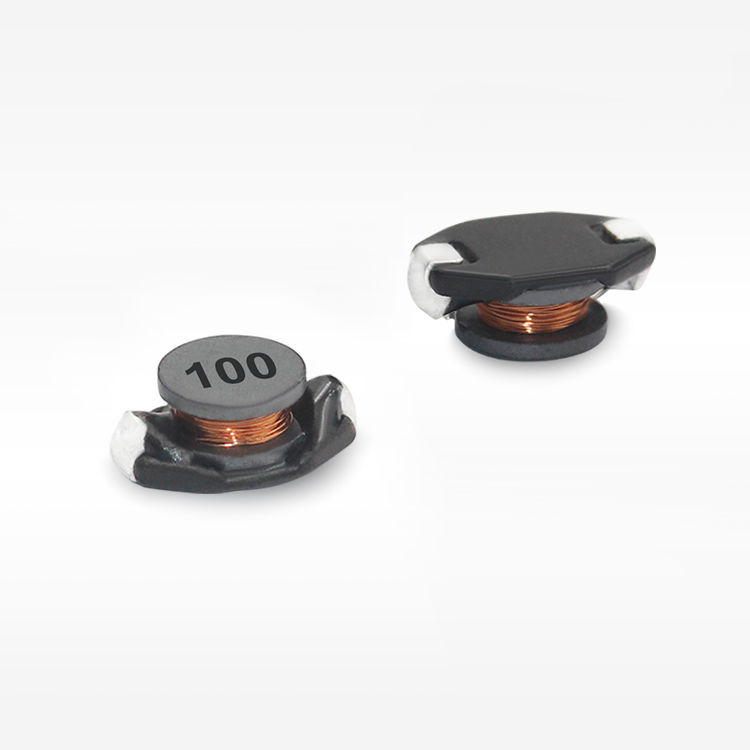
סליל סMD מוגן מייצג רכיב קריטי במעגלים אלקטרוניים מודרניים, שתוכנן לאחסן אנרגיה בשדות מגנטיים תוך שמירה על תאימות אלקטרומגנטית יוצאת דופן. רכיבי שטח קומפקטיים אלו משלבים חומרים מתקדמים ללב מגנטי עם שילוט מדויק מהנדס כדי לספק ביצועים מוכחים ביישומי ניהול כוח. סליל הספק SMD המוגן מאפיין אותו מבנה ליבה מגנטית סגורה שמפחיתה משמעותית הפרעות אלקטרומגנטיות (EMI) ומצמצמת את הדליפת השטף, מה שהופך אותו אידיאלי ללוחות מעגל צפופים שבהם אילוצי שטח ושלמות האות הם עיקריים. היסודות הטכנולוגיים של הסליל המוגן SMD מבוססים על ליבות פרייט או ברזל אבקתי הכלואים בתוך שילוט מגנטי, ויוצרים מעגל מגנטי עצמאי שמונע הפרעות ברכיבים הסמוכים. עיצוב זה מאפשר ערכי השראות גבוהים יותר בנפח קטן יותר, תוך שמירה על תכונות חשמליות יציבות בתנאים משתנים של טמפרטורה ותדרים. תהליכי הייצור של סלילי SMD מוגנים כוללים טכניקות כריכה מדויקות, איסוף אוטומטי ואמצעי ביקורת איכות מחמירים כדי להבטיח עקביות של פרמטרי ביצועים. הפונקציות העיקריות כוללות איחסון אנרגיה, סינון זרם, ניטור מתח וכיבוי רעש בספקי כוח מתחלפים, ממירי DC-DC ומגוון מעגלי ניהול כוח. היישומים משתרעים על פני אלקטרוניקה רכבית, תשתיות תקשורת, אלקטרוניקה לצרכן, מערכות אוטומציה תעשייתית וציוד לאנרגיה מתחדשת. הסליל SMD המוגן מצטיין בסביבות הדורשות אמינות גבוהה, מידות קטנות וביצועים תרמיים מצוינים. תכונות טכנולוגיות עיקריות כוללות התנגדות DC נמוכה ליעילות משופרת, דירוגי זרם הרוויה גבוהים לטיפול חזק בכוח והשראה מעולה של טמפרטורה לפעולת עקביות בטווחים סביבתיים רחבים. השילוט המגנטי מסיר את הצורך בריווח נוסף בין רכיבים, מה שמאפשר ת layouts קומפקטיים יותר של PCB, מצמצם את עלות המערכת הכוללת ומשמר ביצועים אלקטרומגנטיים מיטביים ביישומים אלקטרוניים רגישים.