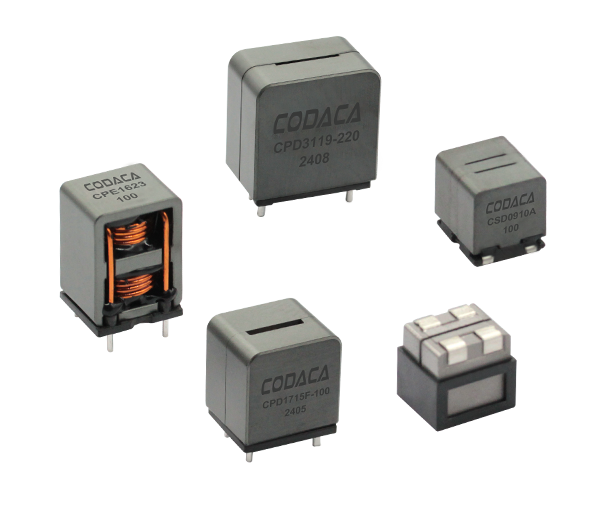
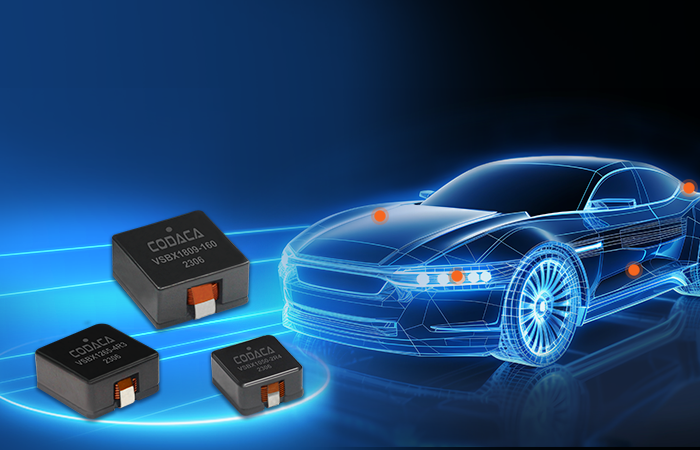
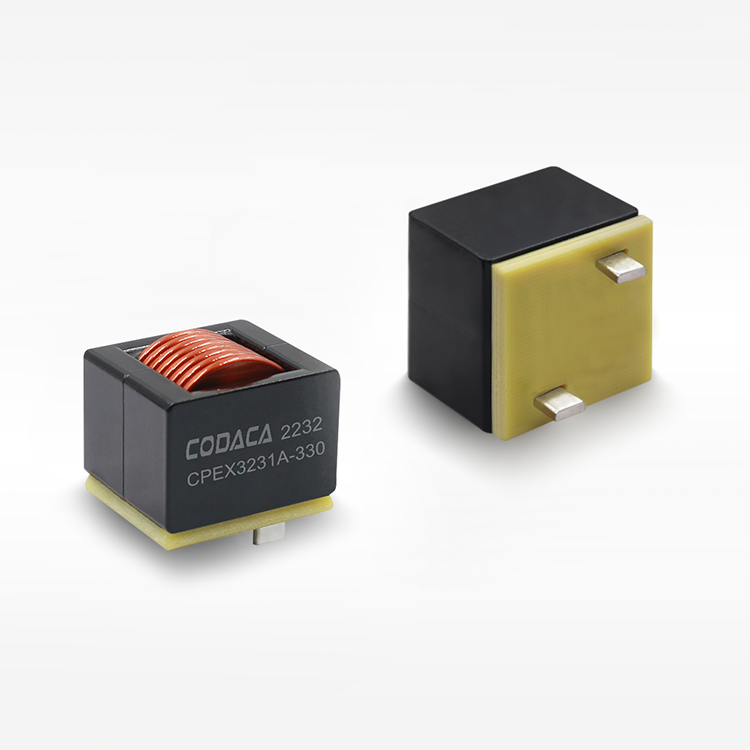
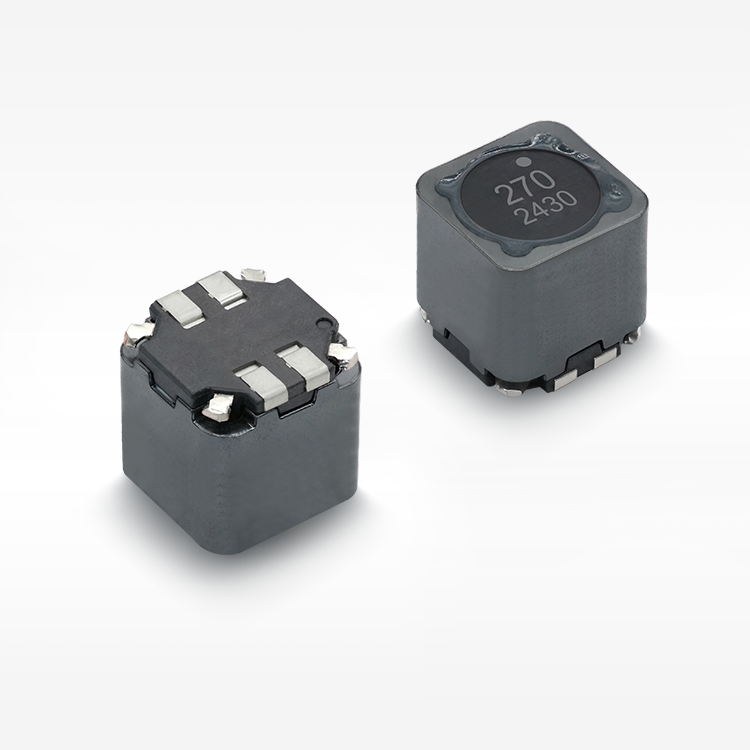
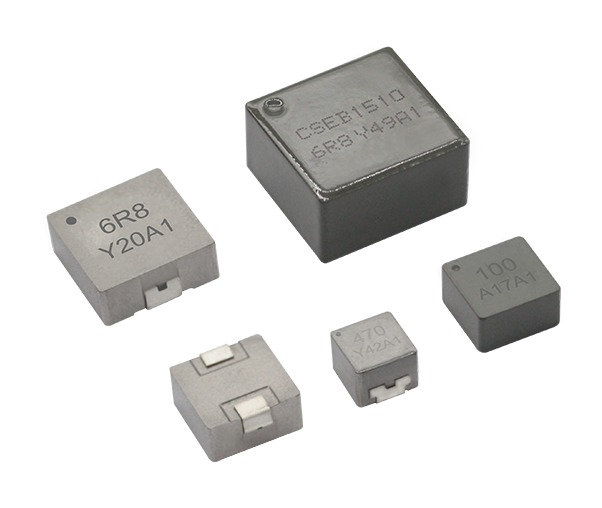
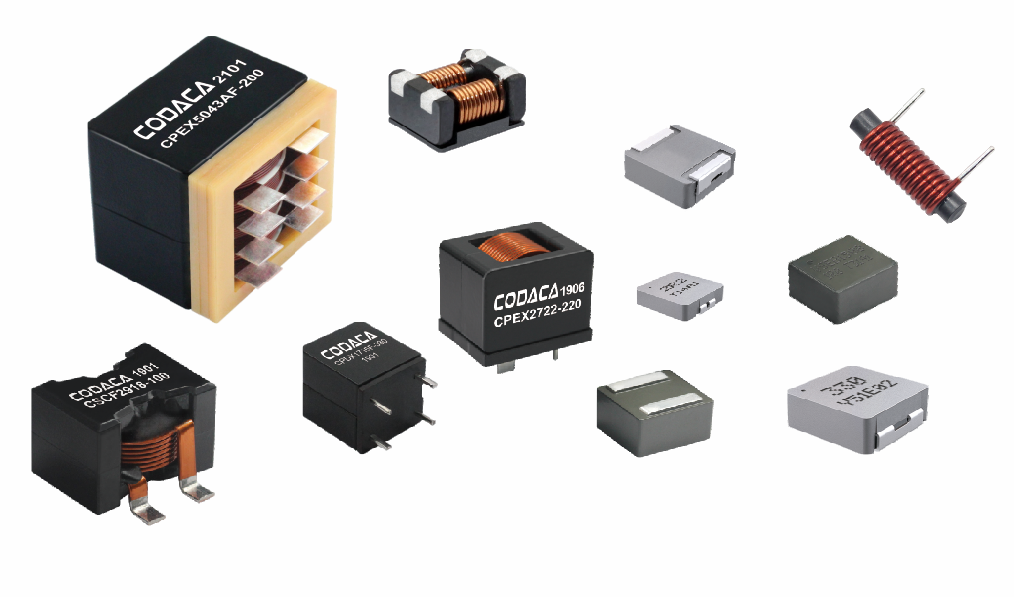
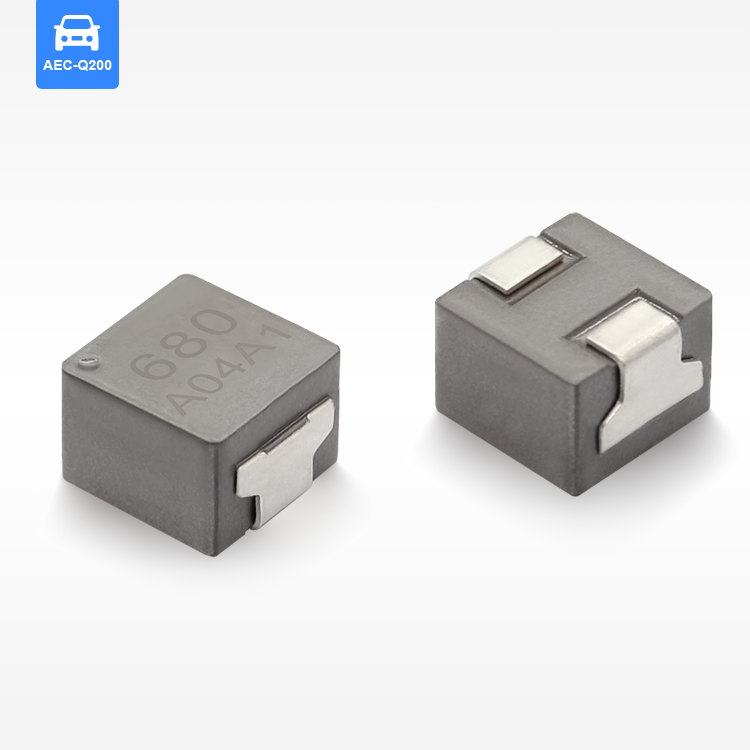
תאימות אלקטרומגנטית וכיבוי הפרעות
היכולות המתקדמות של תיאום אלקטרומגנטי וứcירת הפרעות משולבות בסלילי מפסק זרם גבוה, מספקות למשתמשים יתרונות של שלמות אות גבוהה ודרכי עמידה בתקנות, שחיוניות בסביבות האלקטרוניות המורכבות של ימינו. הסלילים כוללים טכנולוגיות שיקוף מתקדמות ועיצוב מעגלים מגנטיים אופטימליים שמגבילים בהצלחה שדות אלקטרומגנטיים ומצמצמים הפרעות מועלות ומקרינות, ומבטיחים אספקת חשמל נקייה ופער מינימלי על רכיבי המעגל הרגישים. העיצוב האלקטרומגנטי משתמש בגאומטריות ליבה ובתצורות כריכה מהנדסות בקפידה שמפחיתות השראות דליפה ומפחיתות קיבול פראי, מה שמייצר ביצועים טובים בתדרים גבוהים וצמצום הקרנות אלקטרומגנטיות. טכניקות שיקוף מיוחדות, הכוללות ליבות שיקוף מגנטיות ומחסומים מוליכים, מכילות את השדות המגנטיים בתוך מבנה הרכיב, ומניעות הפרעות במעגלים סמוכים וברכיבים רגישים כגון מגברי אנלוג, מעגלי מדידה מדויקים ומודולי תקשורת. המשתמשים נהנים בצורה משמעותית מתכונות התיאום האלקטרומגנטי (EMC) הללו, שמביאות להפחתת הצורך ברכיבי סינון נוספים ובמעטפות שיקוף יקרות, ומאיצות את תהליכי האישור של המוצרים, תוך פשטות באישורים ברמה של המערכת עם התקנות הבינלאומיות בתחום התיאום האלקטרומגנטי. יכולותứcירת ההפרעות עוברות מעבר למגבלות פשוטות, שכן הסלילים מסננים באופן פעיל רעשים בתדר גבוה והרמוניות מפסק שנוצרות על ידי מעגלי המרת אנרגיה, ומייצרות מוצא DC נקי יותר וזרם גלוי מצומצם, מה שמשפר את הביצועים הכולל של המערכת. פעולת הסינון הזו מגינה על רכיבים רגישים ממורד הזרם מפני רעשים של המפסק ומעברי מתח, מחזקת את אמינות המערכת ומקנת חיים ארוכים יותר לרכיבים בכל המערכת האלקטרונית. העיצוב האופטימלי של המעגל המגנטי מספק גם דחיית רעש מצוינת במצב משותף, ומצמצם בצורה יעילה לולאות אדמה והפרעות מועלות שיכולות להתפשט דרך רשתות הפצת החשמל ולהביא לירידה בביצועים בקנה מידה של כל המערכת. המשתמשים מעריכים את הפחתת הצורך ברכיבי סינון EMI חיצוניים, מאחר שיכולותứcירת ההפרעות המובנות בסליל לעתים קרובות מבטלות את הצורך בסינורי מצב משותף נפרדים ומסנני מצב דיפרנציאלי, ומשפשטות את עיצוב המעגלים ומצמצמות את עלויות הרכיבים. תכונות התיאום האלקטרומגנטי תורמות גם לשיפור דיוק המדידה ביישומי מכשירי מדידה מדויקים, כאשר רמת הרעש הנמוכה מאפשרת עיבוד אותות ורכישת נתונים מדויקים יותר. במערכות תקשורת, הביצועים הגבוהים בתחום התיאום האלקטרומגנטי מונעים הפרעות במעגלי רדיו-תדר ומבטיחים עמידה במגבלות חמורות של קרינה אלקטרומגנטית הנדרשות לאישור מכשירים אלחוטיים. יכולות התיאום האלקטרומגנטי והתשכורות ההפרעות המשולבות הללו הופכות את סלילי המפסק בזרם גבוה לאמיתיים ליישומים באלקטרוניקה אוטומotive, ציוד רפואי, מערכות תעופה וחלל ואוטומציה תעשייתית, שבהן דרישות התיאום האלקטרומגנטי הן szczególnie קפדניות ואמינות המערכת היא בעלת חשיבות עליונה.