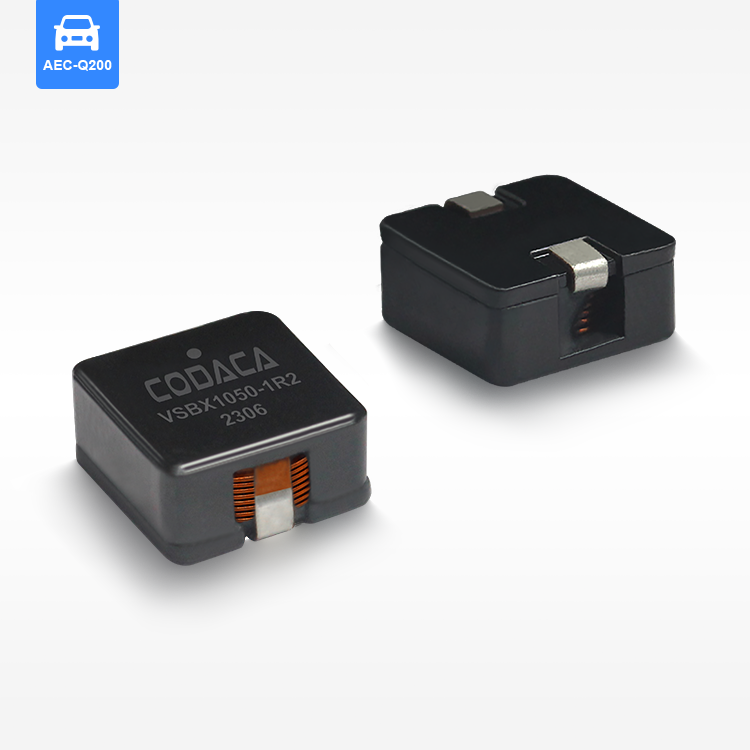
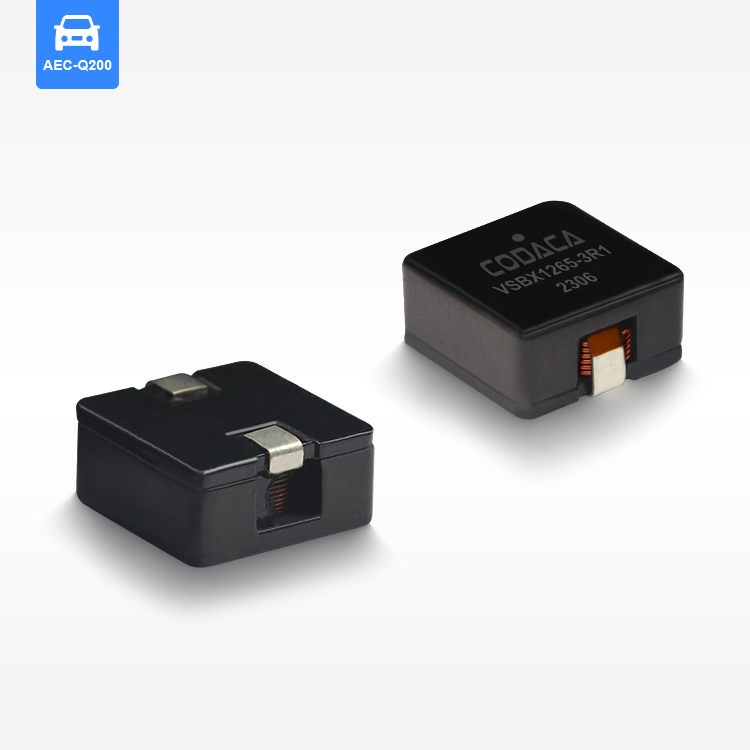
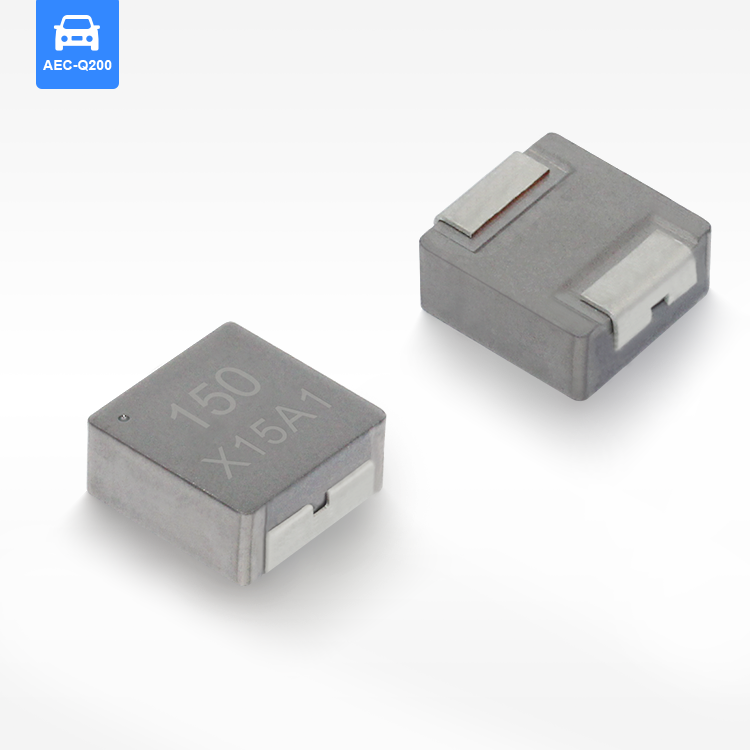
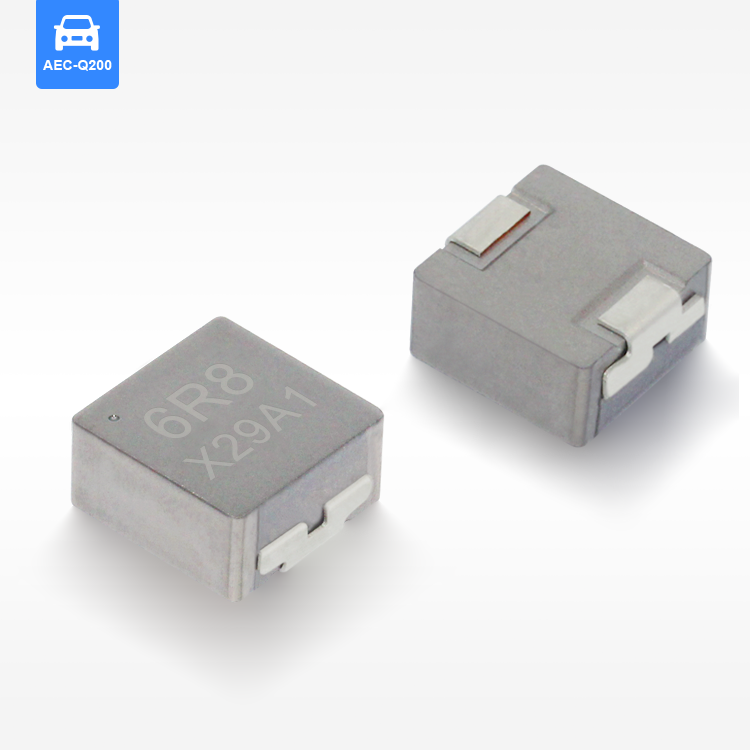
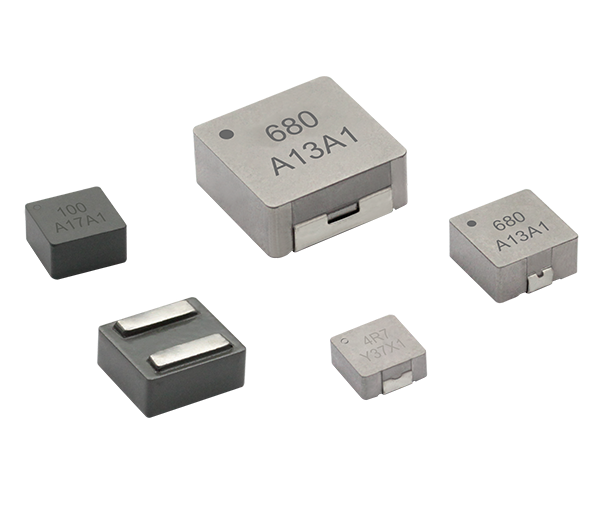
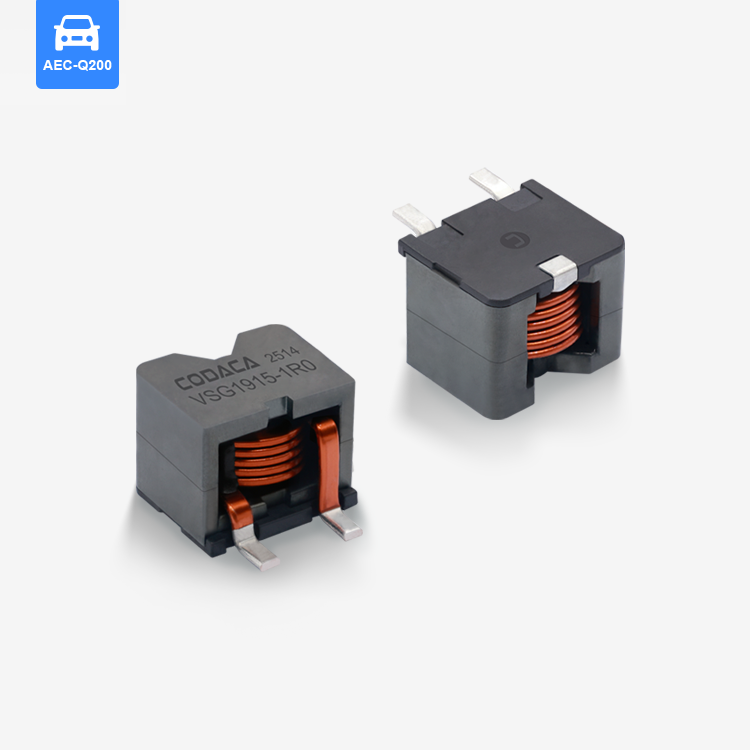
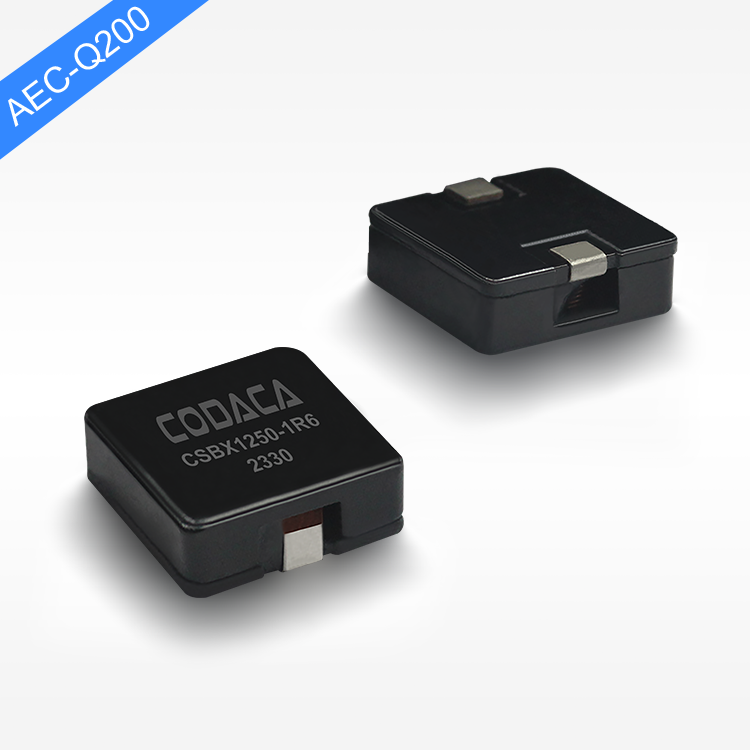
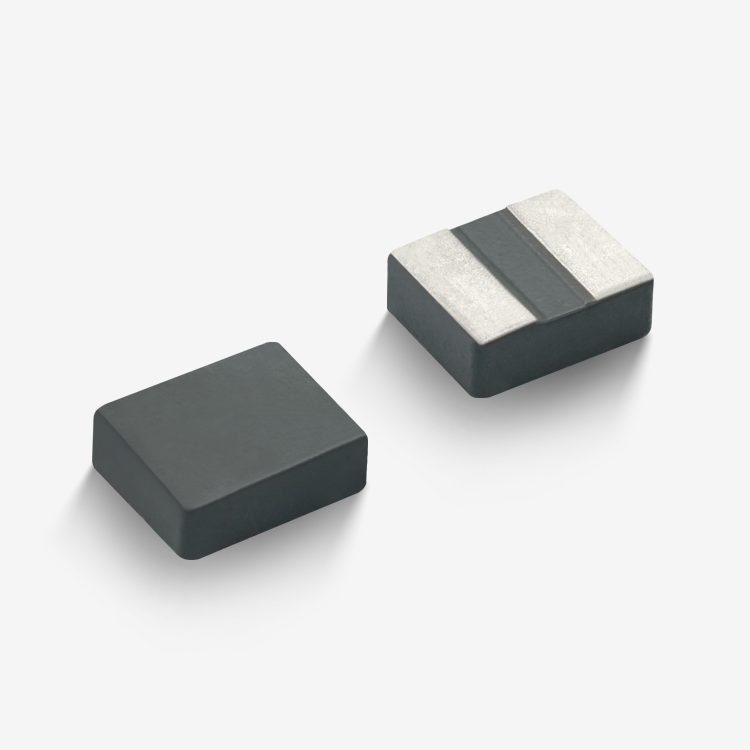
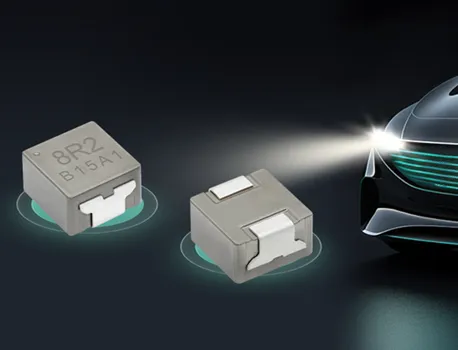
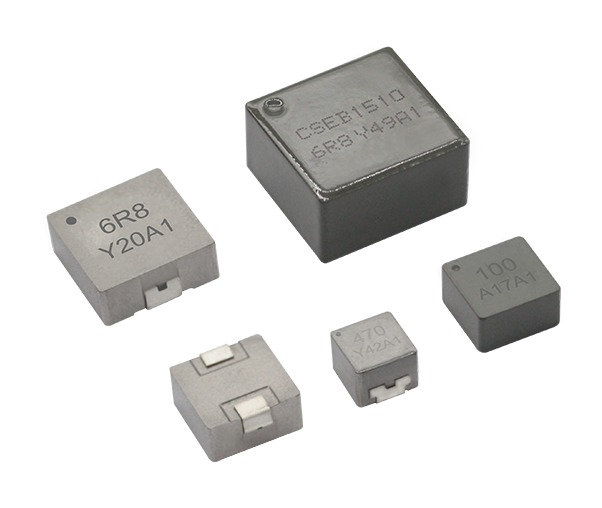
toroidal endüktans
Toroidal endüktans, elektromanyetik bileşen tasarımında devrim niteliğinde bir gelişmeyi temsil eder ve modern elektronik uygulamalar için vazgeçilmez bir seçim haline getiren üstün performans özelliklerine sahiptir. Bu özel indüktör, iletken tel sargılarla sarılmış bir simit şeklindeki ferromanyetik malzemeden oluşan toroidal bir çekirdek yapısını kullanır. Toroidal endüktansın benzersiz geometrik yapısı, verimliliği önemli ölçüde artıran ve elektromanyetik gürültüyü en aza indiren kapalı bir manyetik döngü oluşturur. Toroidal endüktansın temel işlevleri arasında manyetik alanlarda enerji depolama, akım filtreleme, voltaj regülasyonu ve çeşitli frekans aralıklarında sinyal işleme yer alır. Bu bileşenler, hassas elektronik cihazlara kararlı güç sağlanması için DC çıkışları düzeltip dalgalanma gerilimini azaltan güç kaynağı devrelerinde özellikle başarılıdır. Toroidal endüktansın teknolojik özellikleri, manyetik akıyı toroidal yapı içinde odaklayarak kaçak alanların oluşmasını engelleyen ve kayıpları azaltan yenilikçi çekirdek tasarımından kaynaklanır. Bu yapı, geleneksel hava çekirdekli veya çubuk çekirdekli indüktörlere kıyasla daha küçük boyutlarda daha yüksek endüktans değerleri elde edilmesini mümkün kılar. Sargılar, toroidal çekirdek etrafında eşit şekilde dağıtılmış olup, çalışma sırasında homojen manyetik alan dağılımı sağlar ve sıcak noktaların oluşumunu en aza indirir. Ferrit, toz demir veya amorf metaller gibi gelişmiş malzemeler çekirdek materyali olarak kullanılır ve bunların her biri farklı frekans aralıkları ile güç seviyeleri için uygun belirli geçirgenlik özelliklerine sahiptir. Üretimdeki hassasiyet, endüktans toleransı, kalite faktörü ve doyum akımı değerleri dahil olmak üzere elektriksel parametrelerin tutarlı olmasını garanti eder. Toroidal endüktansın uygulamaları tüketici elektroniğinden endüstriyel otomasyon sistemlerine kadar birçok sektörde yer alır. Anahtarlamalı güç kaynaklarında bu bileşenler, minimum elektromanyetik gürültü üretimiyle verimli voltaj dönüşümüne olanak tanıyan temel filtreleme ve enerji depolama işlevlerini üstlenir. Ses ekipmanları, özellikle yüksek sadakat amplifikatörler ve crossover ağlarında, toroidal endüktans sayesinde sinyal netliğinde iyileşme ve bozulmada azalma sağlar. Telekomünikasyon altyapısı, veri iletim sistemlerinde empedans uyumu, sinyal kuplajı ve gürültü bastırması için toroidal endüktansa güvenir. Tıbbi cihazlar, hassas akım kontrolü ve hasta güvenliği izolasyonu amacıyla bu indüktörleri kullanır. Otomotiv elektroniği, motor yönetim sistemlerinde, direksiyon kontrol sistemlerinde ve elektronik uyumluluk ile güvenilirliğin kritik gereklilikler olduğu hibrit araç inverterlerinde toroidal endüktansı kullanır.