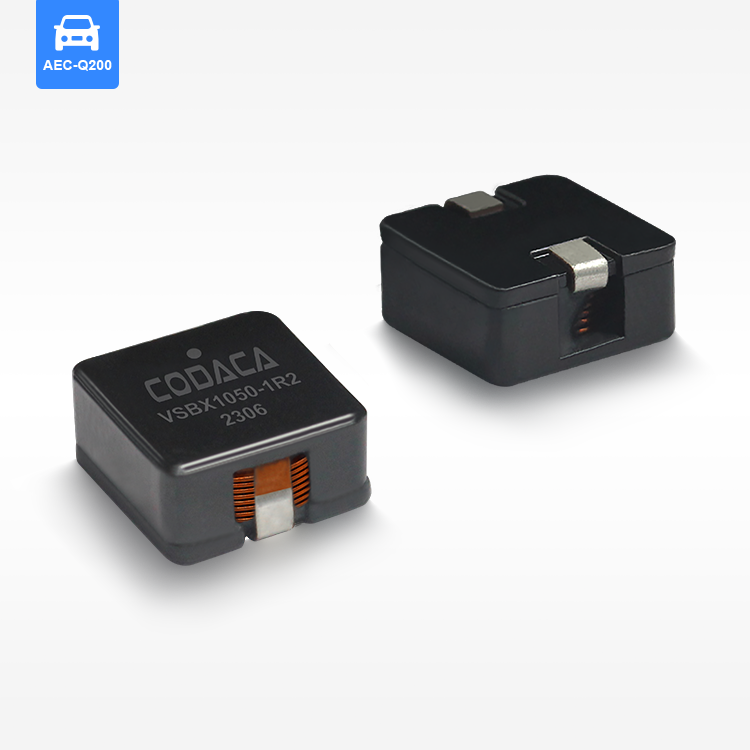
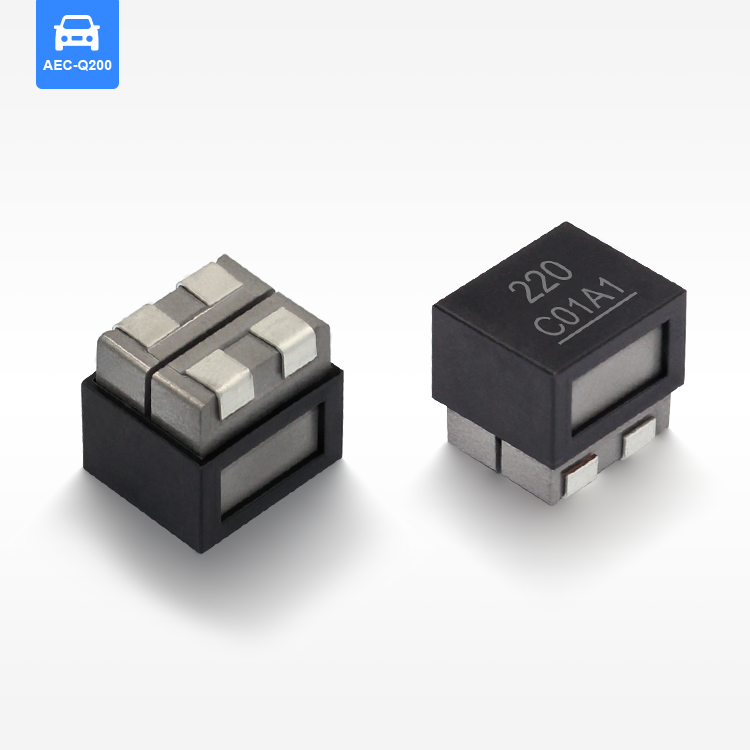
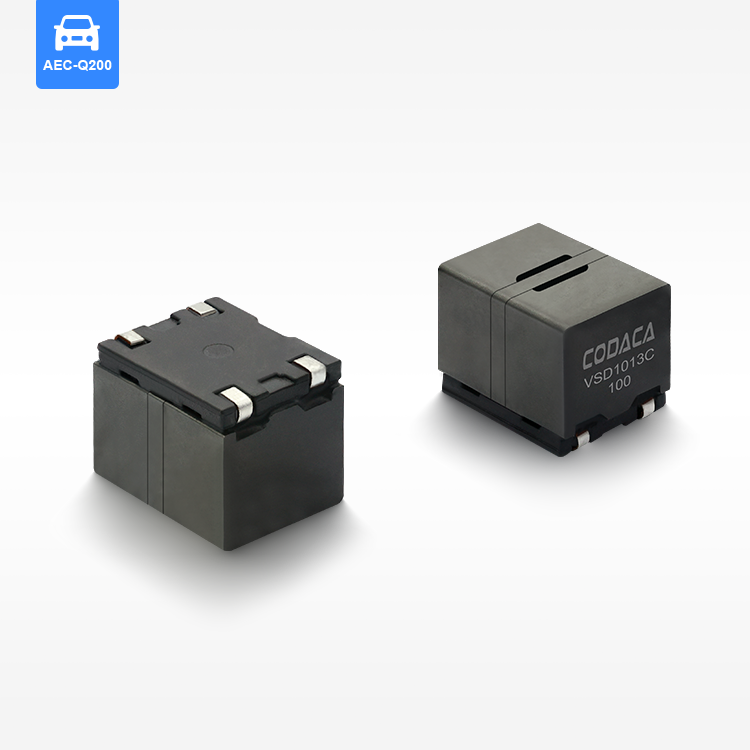
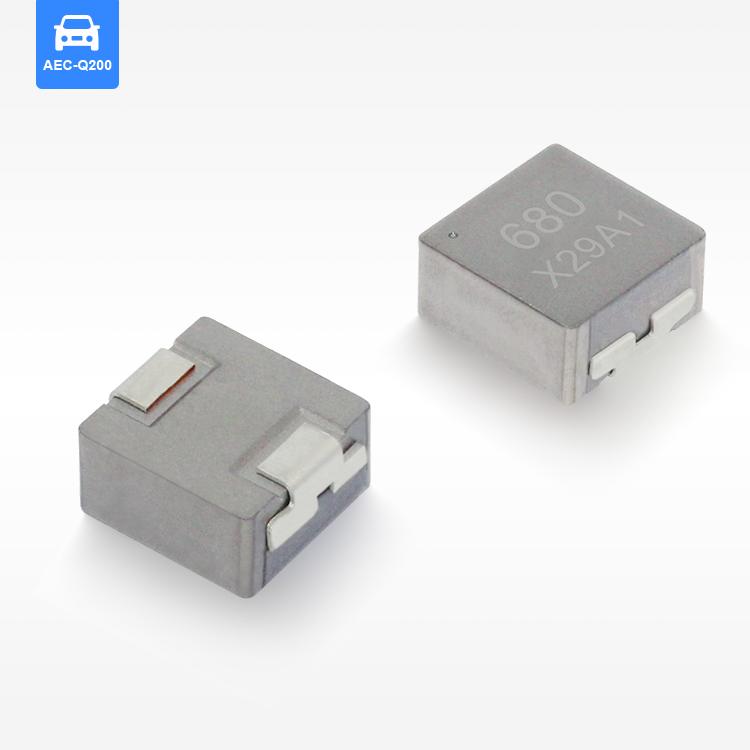
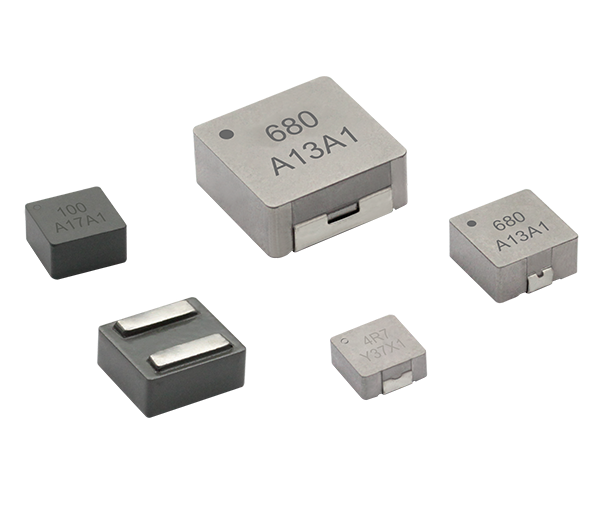
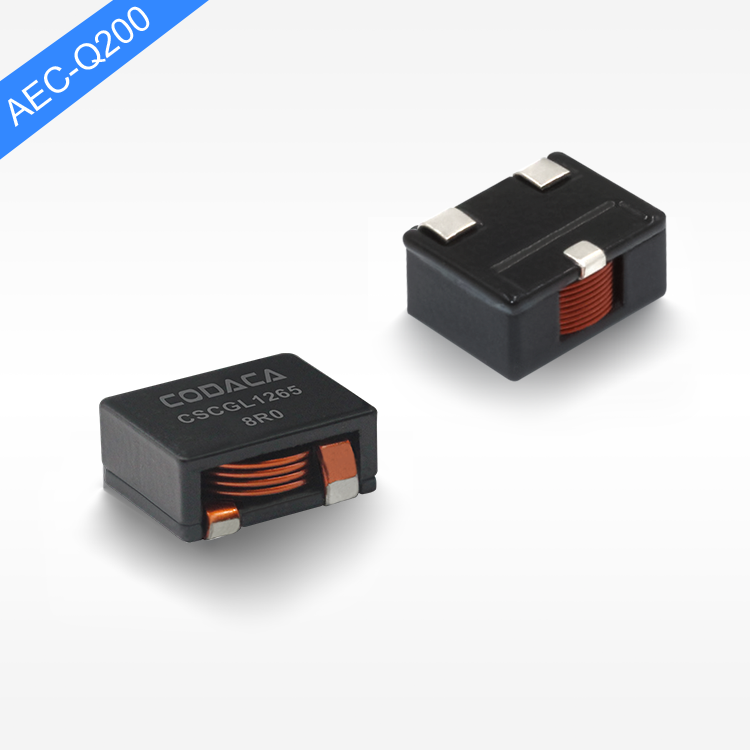
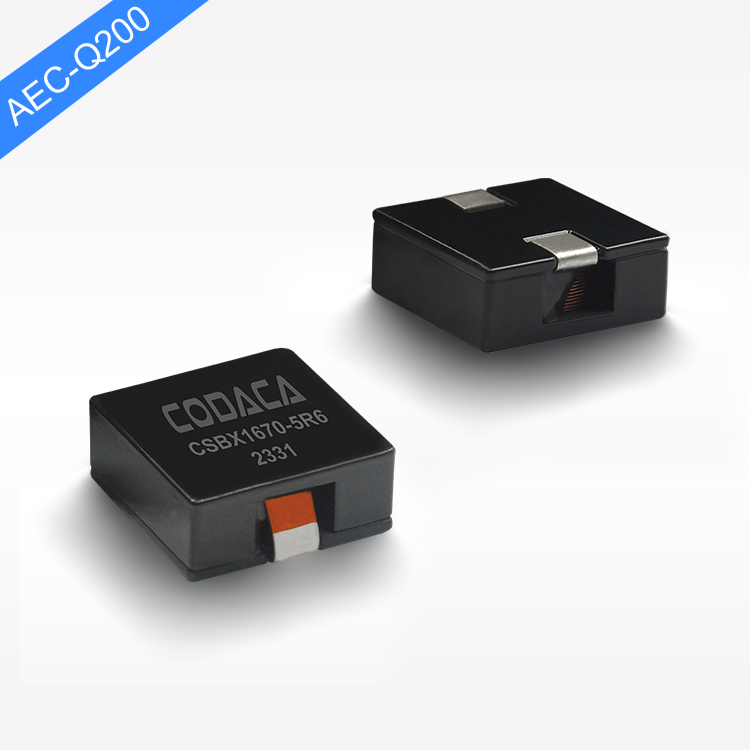
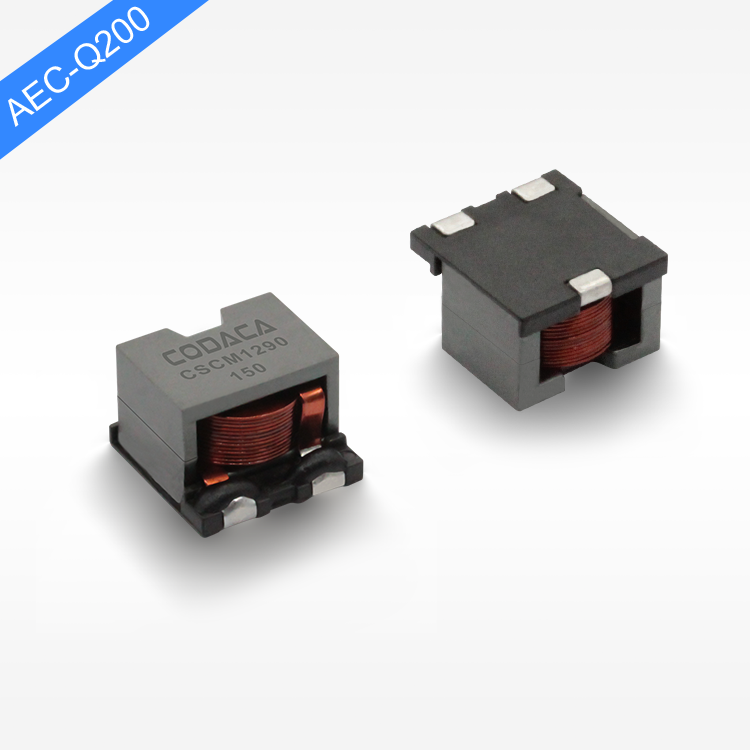
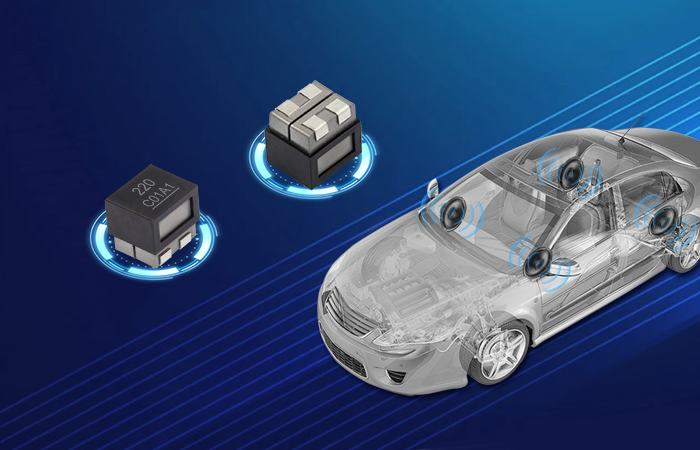
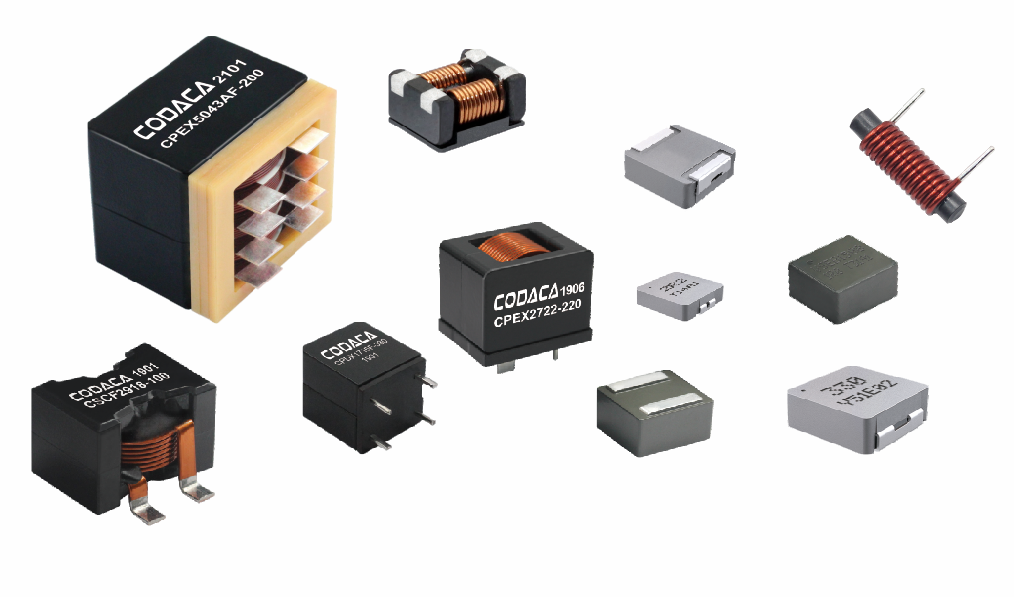
flat wire high current inductor
The flat wire high current inductor represents a revolutionary advancement in electromagnetic component technology, designed specifically to handle substantial electrical loads while maintaining exceptional efficiency and reliability. This innovative inductor utilizes flat copper wire construction instead of traditional round wire, creating a component that delivers superior performance in high-current applications. The flat wire high current inductor serves multiple critical functions in electronic systems, primarily acting as an energy storage device that smooths current flow and reduces electromagnetic interference. Its primary technological feature lies in the unique flat wire winding configuration, which maximizes conductor surface area while minimizing resistance and heat generation. This design allows the flat wire high current inductor to handle significantly higher current levels compared to conventional inductors of similar size. The component operates by storing energy in its magnetic field when current flows through the windings, then releasing this energy back into the circuit as needed. This fundamental operation makes the flat wire high current inductor essential for power management applications, DC-DC converters, and switching power supplies. The technological sophistication extends to its core materials, typically featuring high-permeability ferrite or powdered iron cores that enhance magnetic field strength and improve overall performance. Applications for the flat wire high current inductor span across multiple industries, including automotive electronics, renewable energy systems, industrial automation, telecommunications infrastructure, and consumer electronics. In electric vehicles, these inductors manage power conversion between batteries and motors, while in solar inverters, they ensure smooth power delivery from panels to the grid. The compact design of the flat wire high current inductor makes it particularly valuable in space-constrained applications where traditional inductors would be impractical. Manufacturing processes involve precise winding techniques that maintain consistent spacing and optimal magnetic coupling, resulting in predictable electrical characteristics and enhanced reliability across varying operating conditions.