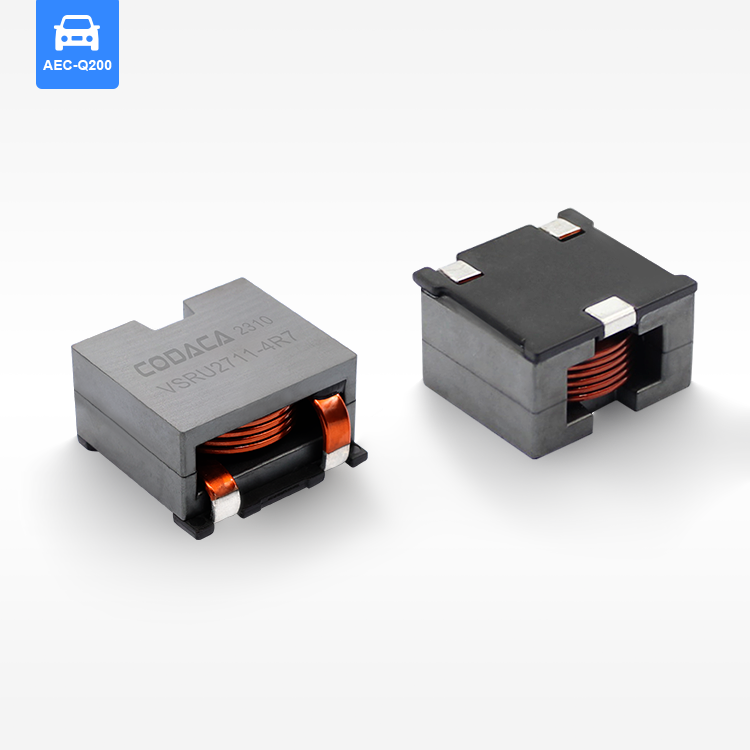
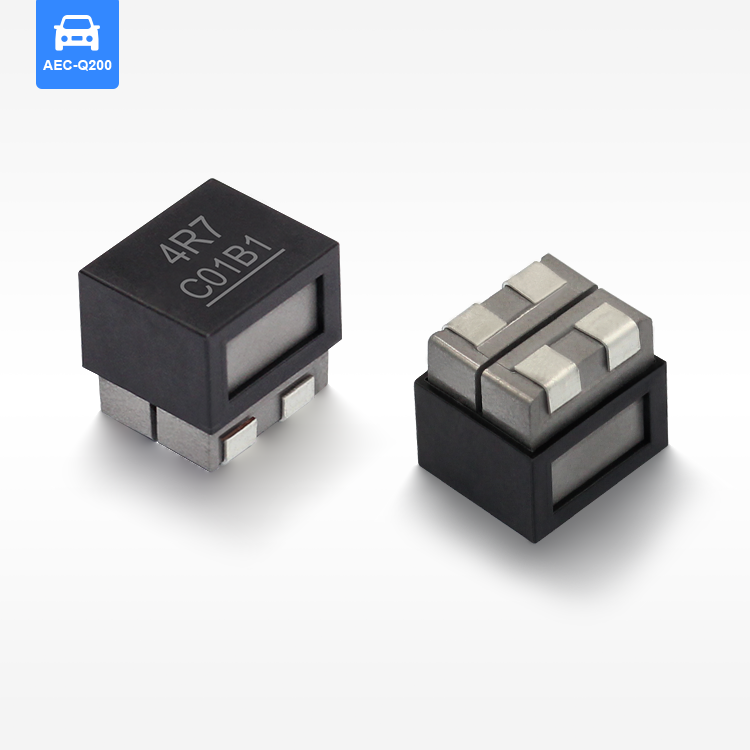
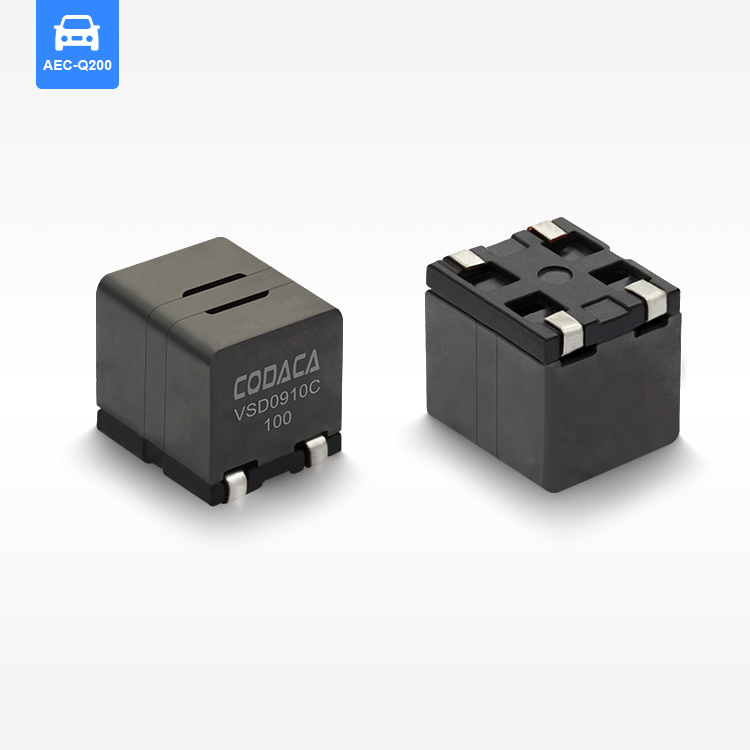
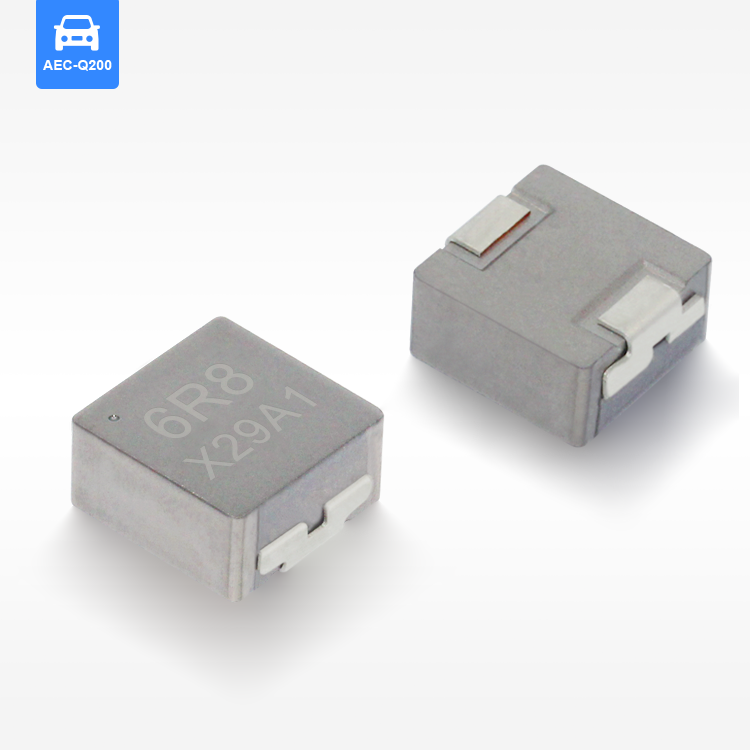
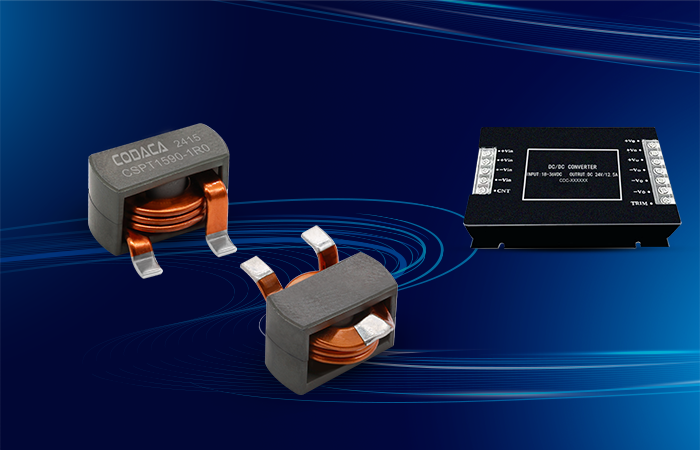
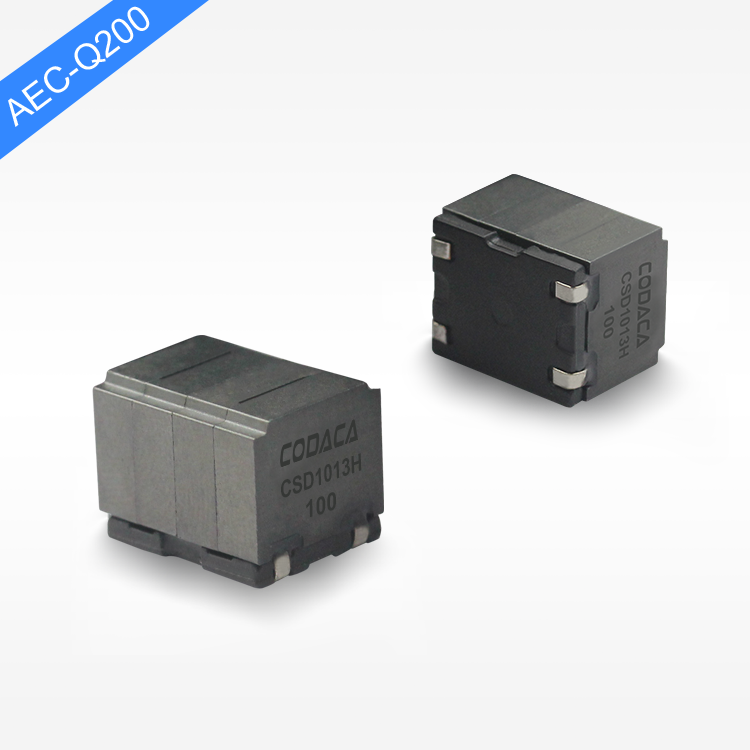
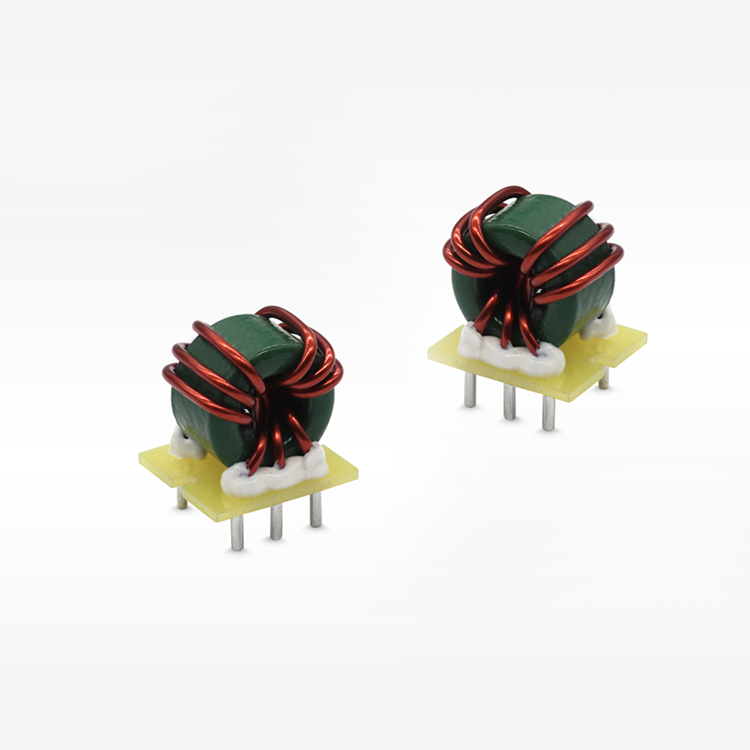
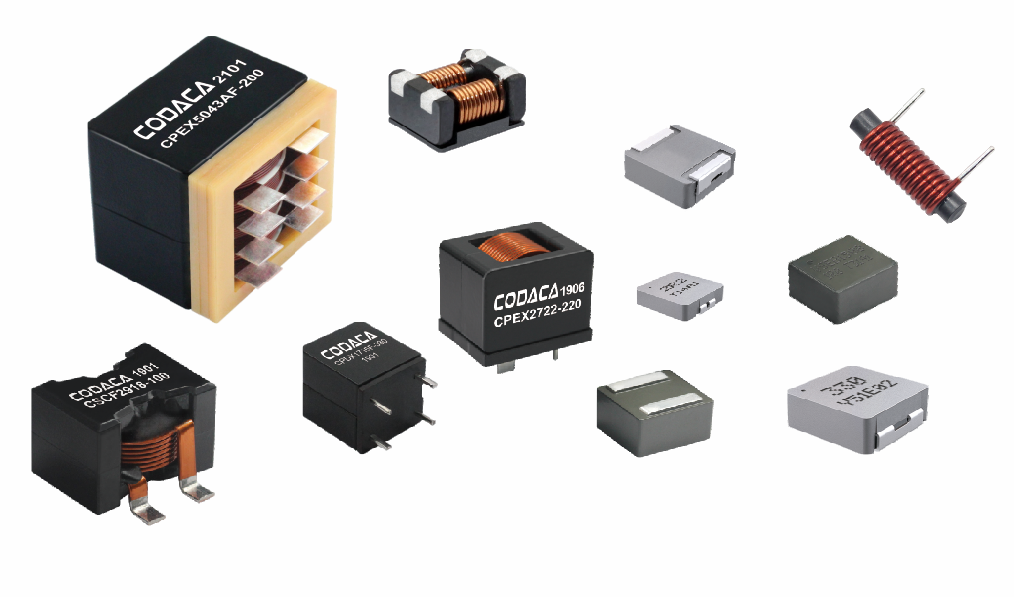
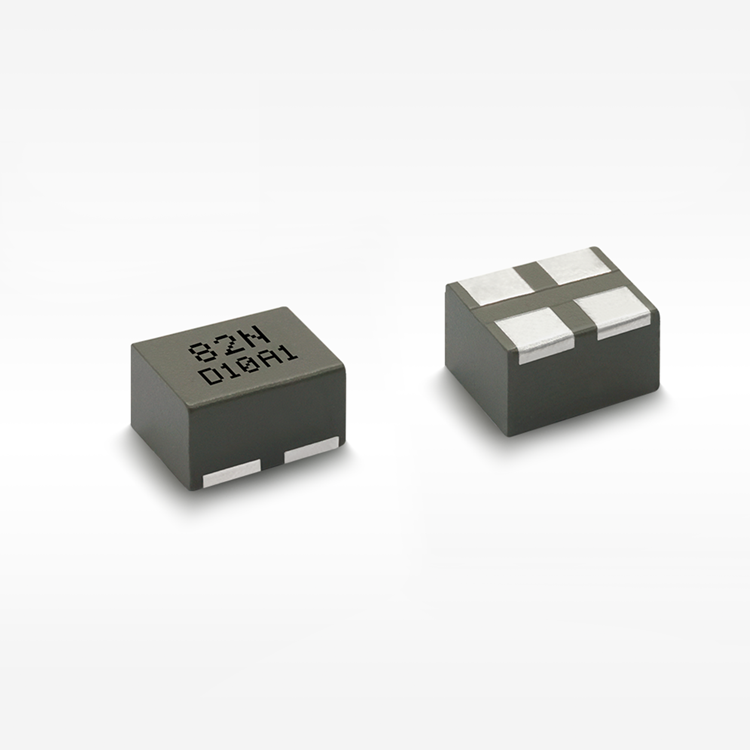
high current low resistance inductor
A high current low resistance inductor is an essential electronic component designed to handle substantial electrical currents while maintaining minimal resistance levels. These specialized inductors serve as energy storage devices that create magnetic fields when current flows through their coils, enabling efficient power management in various electronic systems. The primary function of a high current low resistance inductor involves filtering electrical signals, smoothing power supplies, and storing energy in switching circuits. Unlike conventional inductors, these components excel in high-power applications where current levels can reach several amperes or even hundreds of amperes. The technological features of high current low resistance inductors include advanced core materials such as ferrite, iron powder, or specialized alloys that enhance magnetic permeability while reducing core losses. The winding construction utilizes thick copper wire or multiple parallel conductors to minimize resistance and handle high currents effectively. Many designs incorporate innovative cooling mechanisms, including heat sinks or thermal pads, to dissipate generated heat during operation. These inductors maintain stable inductance values across varying current levels, ensuring consistent performance in demanding applications. The low resistance characteristic, typically measured in milliohms, reduces power losses and improves overall system efficiency. Applications for high current low resistance inductors span across numerous industries and electronic systems. Power supplies rely on these components for output filtering and energy storage, while DC-DC converters utilize them for voltage regulation and current smoothing. Electric vehicle charging systems incorporate high current low resistance inductors to manage power flow safely and efficiently. Renewable energy systems, including solar inverters and wind power converters, depend on these inductors for power conditioning and grid synchronization. Industrial motor drives, welding equipment, and battery management systems also benefit from their superior current handling capabilities and minimal resistance characteristics.