עם ההתפתחות המהירה של אנרגיה מבוזבזת, מערכות איחסון אנרגיה לבית ה стали חשובות יותר ויותר לשיפור יעילות ניצול האנרגיה ולשיפור יציבות אספקת החשמל. כרכיב מרכזי במערכות איחסון אנרגיה לבית, משדרים דו-כיווניים של DC-DC ממלאים תפקיד חשוב בהשגת זרימת אנרגיה דו-כיוונית יעילה וגמישה בין סוללות, רשת החשמל או העומסים. בין הרכיבים השונים של משדרי DC-DC דו-כיווניים, מוליכי כוח בת}elseif גבוה ממלאים תפקיד חשוב במיוחד, וביצועיהם משפיעים ישירות על היעילות, היציבות והאמינות הכוללת של המשדרים.

1- סקירה של עיקרון הפעולה של משדרי DC-DC דו-כיווניים ב בית מערכות אחסון אנרגיה
ממכפלי DC-DC דו כיווניים יכולים להעביר אנרגיה בין רמות מתח DC שונות. במצב טעינה, הם הופכים את המתח הגבוה יותר מהרשת או מקורות פוטו-וולטאיים למתח נמוך יותר המתאים לטעינת סוללות לאחסון אנרגיה. במצב של פינוי, הם מגבירים את מתח הסוללה הנמוך יותר למתח גבוה יותר אשר עומד בדרישות עומס או יכול להיות מופץ בחזרה לרשת. אם ניקח לדוגמה את המרת DC-DC דו-כיוונית של סוג Buck-Boost, במצב של Buck step-down, כאשר מתג החשמל (MOSFET) פועל, אספקת החשמל ההובלת מספקת חשמל לטען דרך האינדוקטור, מגדילה את זרם האינדוקטור ומאחסן אנ כאשר המתג כבוי, זרם האינדוקטור ממשיך לזרום אל העומס באמצעות דיודה מתגלגלת חופשית (או מתקן סינכרוני), משחרר את האנרגיה המאוחסנת שלו, ובכך משיגים אספקת חשמל מתמשכת לעומס במהלך תקופות כבוי. במצב Boost step-up, כאשר המתג מופעל, אספקת החשמל נכנסת לטען את האינדוקטור, אשר מאחסן אנרגיה. כאשר המתג כבוי, האינדוקטור ומספק החשמל נכנסים יחד כדי להגדיל את מתח היציאה.
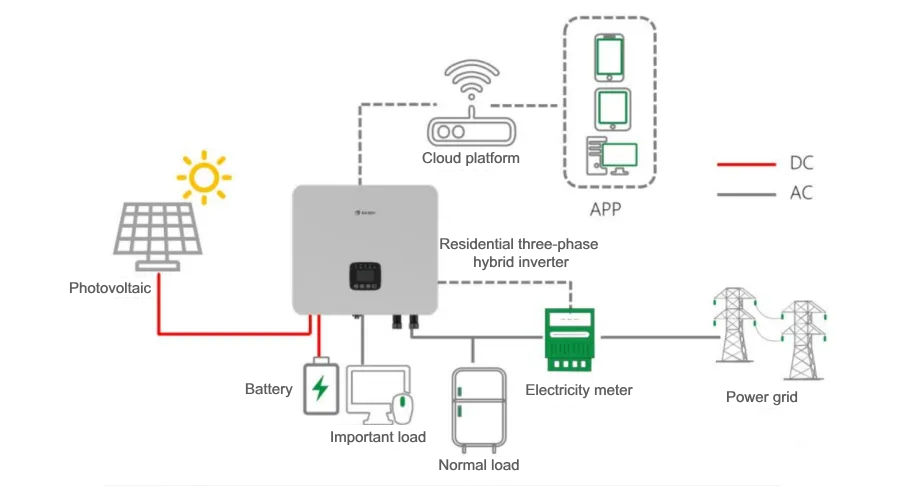
איור 1. דיאגרמת תרחיש יישום של אגירת אנרגיה למגורים
2- התפקיד של סלילי הספק בממירי DC-DC דו-כיווניים
סלילי הספק ממלאים תפקיד מרכזי בממירי DC-DC דו-כיווניים כרכיבים מרכזיים לאגירת והעברת אנרגיה. בשלב הפעלה, זרם הסליל גדל בהדרגה, והאנרגיה החשמלית מאוחסנת בתוך הסליל כאנרגיה מגנטית. כאשר המפסק מכובה, זרם הסליל קטן, והאנרגיה המגנטית מומרת חזרה לאנרגיה חשמלית, מה שמבטיח רציפות של הזרם במעגל ומאפשר המרת מתח כלפי מעלה או למטה. dado שסלילי הספק בממירי DC-DC דו-כיווניים פועלים בעיקר בסביבות של זרם גלי גבוה, מה שיוצר איבודים משמעותיים, ניתן להפחית את איבודי DCR של הסליל ולהגביר את תדירות הפעולה על מנת לשלוט באיבודים בתנאי זרם גלי גבוה.
3- השפעת סלילי הספק על ממירי DC-DC דו-כיווניים
3.1 ערך האינדוקטיביות
הערך של ההשראות משפיע ישירות על יחס המרת המתח, רעמת הזרם וسرعة התגובה הדינמית של הממיר. כאשר ערך ההשראות גדול, רעמת הזרם קטנה, מה שמאפשר למתח הפלט להיות חלק יותר, וכן תורם לשיפור היעילות והיציבות של הממיר. עם זאת, ערך השראות גדול מדי עלול להאט את התגובה הדינמית של הממיר, כך שלא יוכל להתאים במהירות את מתח הפלט בעת שינוי העומס. כאשר ערך ההשראות קטן מדי, גם אם התגובה הדינמית מהירה, רעמת הזרם גדולה, מה שגובר על איבדי התקן החשמלי, מוריד את יעילות הממיר, ואף עלול לגרום לעירור מעגל, וכך לפגוע בפעולה התקינה של המערכת. בעיצוב מעשי, יש לבדוק באופן מקיף את מצב הפעולה של הממיר, מאפייני העומס ודרישות הביצועים, כדי לבחור בצורה מדויקת את ערך ההשראות.
3.2 זרם סחיקה
כאשר הזרם דרך הסליל גדול מדי, צפיפות השטף המגנטי של הליבה מגיעה לערכה של רוויה, והסליל נכנס למצב רווית מغנטית, וערך ההשראות יורד בצורה חדה. במרביך DC-DC דו-כיווניים, רווייה מגנטית של הסליל עלולה לגרום לשליטה אבודה בזרם, עלייה משמעותית ברעשים ושיבוש בהתקני החשמל עקב זרם יתר, מה שמשפיע בצורה חמורה על התפעול התקין של המהפך. כדי להימנע מרוויה מגנטית, יש לתכנן באופן הגיוני את חומר הליבה ואת גודלה, כדי להבטיח שהסליל לא יכנס לרוויה תחת הזרם המרבי בתנאי פעולה. במקביל, ניתן לאמץ שיטות כגון הגדלת הפערים באוויר כדי להרחיב את טווח העבודה הליניארי של הסליל ולשפר את האמינות של המהפך. Codaca פיתח באופן עצמאי מספר סדרות של מוליכי זרם גבוה ליבת אבקה מגנטית, המשתמשים בליבות אבקה מגנטית עם תערובת פטנטית כדי לשפר את מאפייני הסättורציה של המוליכים.
3.3 התנגדות ישרה (DCR)
התנגדות ה-DC מתייחסת להתנגדות הפנימית של סליל המוליך בתנאי זרם ישר. ככל שה-DCR נמוך יותר, כך אובדת פחות אנרגיה כאשר זורם זרם, ובכך מושגת יעילות כוללת גבוהה יותר.
בבחירת המוצר, עדיפו מוצרים עם מאפייני DCR נמוך כדי להפחית איבודי העברה ולשפר את יעילות הממיר.
3.4 תדר פעולה
הגדלת תדר המיתוג של ממירים דו-כיווניים מסוג DC-DC יכולה להפחית את גודל רכיבי הפסיביים כגון סלילים וקבלים, ולשפר את צפיפות ההספק ואת מהירות התגובה הדינמית של הממיר. עם זאת, כאשר סלילים פועלים בתדרים גבוהים, השפעת הפרמטרים הסיטתיים מחריפה, והאפקט של קליפת העור והאפקט הקירبي גורמים לעליה משמעותית באובדי הסליל. חומרי מגנט מסורתיים עשויים שלא לעמוד בדרישות, מה שמגביר בעיות כגון חימום הנובע מאובדן ליבה. לכן, בחירת מוצרים של סלילים לשימוש בתדרים גבוהים היא שלב חשוב להבטחת פעולת המערכת היציבה.
3.5 טמפרטורת עבודה
מערכות אגירת אנרגיה ביתיות פועלות בסביבות מורכבות, הדורשות סלילי כוח בעלי תכונות פיזיקליות מצוינות ויכולת הסתגלות סביבתית. גודל ומשקל הסליל חייבים לעמוד בדרישות התכנון הקומפקטי של ציוד אגירת אנרגיה ביתי. בסביבות קשות כמו טמפרטורות גבוהות ולחות, הסליל צריך לשמור על ביצועים יציבים, עם חומרי ליבה שאינם מושפעים בקלות מטמפרטורה ולחות, ולהפגין ביצועי פיזור חום טובים יחד עם עמידות בפני לחות, עובש וקורוזיה. בבחירה, עדיף לבחור סלילי פעולה בטמפרטורה גבוהה עם מאפייני הטיה של טמפרטורה נמוכה ו-DC, כגון מוצרי ליבת פריט בעלי זרם גבוה.
4- פתרונות של Codaca להמרני DC-DC דו-כיווניים לאחסון אנרגיה ביתי
Codaca סיפקה מספר פתרונות של מוליכי השראה מתואמים להמרני DC-DC דו-כיווניים לשימוש ביתי, באמצעות פיתוח עצמאי וחדשנות טכנולוגית, ובכך תרמה לפיתוח ירוק ונמוך פחמן. CODACA הושיקה מספר דגמים של מוליכי הספק בתוספת זרם גבוה, עם מאפיינים חשמליים שונים ועיצובי אריזה מגוונים, כדי לעמוד בדרישות הביצועים הגבוהות של מוליכי ההשראה ליישום זה. בין היתר, מוליך ההשראה בתוספת זרם גבוה שפותח באופן עצמאי על ידי Codaca, ליבת הפודרה המגנטית שלו מצטיינת בזרם הסתuration גבוה, אובדן נמוך, יעילות המרה גבוהה וטמפרטורת עבודה גבוהה, ועונה בכך לדרישות של מערכת המרת DC-DC דו-כיוונית לשימוש ביתי מבחינת זרם עבודה גבוה, אובדן נמוך וצפיפות הספק גבוהה.

איור 2. מוליך השראה של Codaca עם זרם גבוה
כרכיב מרכזי במשתננים דו-כיווניים ייחודיים לDC-DC, שוחות הספק ממלאות תפקיד בלתי ניתן להחלפה באחסון והמרת אנרגיה, וכן בדיכוי גלי זרם. הביצועים שלהן משפיעים ישירות על היעילות, היציבות והאמינות של המשתננים. עם ההתקדמות המתמדת בטכנולוגיית איחסון אנרגיה ביתית, דרישות הביצועים לשוחות הספק נעשות מחמירות יותר, כאשר צפיפות הספק הגבוהה, פעולת התדר הגבוהה והאינטגרציה עולות כמגמות מפתח לפיתוח. בתגובה לאתגרים אלו, Codaca Electronics מבצעת מחקר מעמיק בתחומים כגון פיתוח חומרי ליבת מגנט ותכנון מיטוב המבנה, כדי לשפר באופן מתמיד את ביצועי שוחות הספק, ומספקת תמיכה איתנה לשיפור הביצועים ולחדשנות טכנולוגית במשתננים דו-כיווניים ייחודיים לDC-DC. זה מסייע לקדם יישומים רחבים ויעילים יותר של מערכות איחסון אנרגיה ביתיות בתחום האנרגיה המופצת.