With the rapid development of artificial intelligence and big data technologies, AI servers, as compute-intensive devices, undertake critical tasks in fields such as cloud computing, deep learning, autonomous driving, and intelligent robots. The performance and stability of AI servers largely depend on the design of their power systems. As computing power demands continue to rise, traditional power architectures are gradually struggling to meet the needs for efficient and stable power supply, leading to the gradual emergence of advanced power architectures, such as 48V distributed power supply, multi-phase buck conversion, and digital control, as mainstream solutions.
1- Main Power Architectures of AI Servers
1.1 Centralized Power Architecture
Traditional centralized power supplies employ a single power supply unit (PSU) to convert AC power into 12V DC power, which is then distributed to various loads through the motherboard. They have a mature design, low cost, and are easy to manage uniformly. However, as the computing power of AI servers increases, their drawbacks become apparent: the long 12V transmission path leads to a significant increase in conduction loss (I²R); the voltage regulation bandwidth is limited, affecting dynamic response speed; it is difficult to cope with the nanosecond-level drastic load changes of CPU/GPU; the system redundancy is poor, and a single power module failure may lead to the entire system crashing, lacking reliability.
1.2 Distributed Power Architecture (DPA)
Distributed power architecture has become the preferred choice for large AI servers. Its core is the use of a 48V intermediate bus power supply. PSUs output 48V DC, leveraging the characteristics of high transmission voltage and low transmission current to significantly reduce energy losses in the distribution paths. Near core loads like CPUs and GPUs, Point-of-Load converters (POLs) are deployed to directly convert 48V to the required low voltages (e.g., 0.8V-1.8V), achieving localized and refined power supply, which greatly enhances transient response speed and voltage regulation precision.
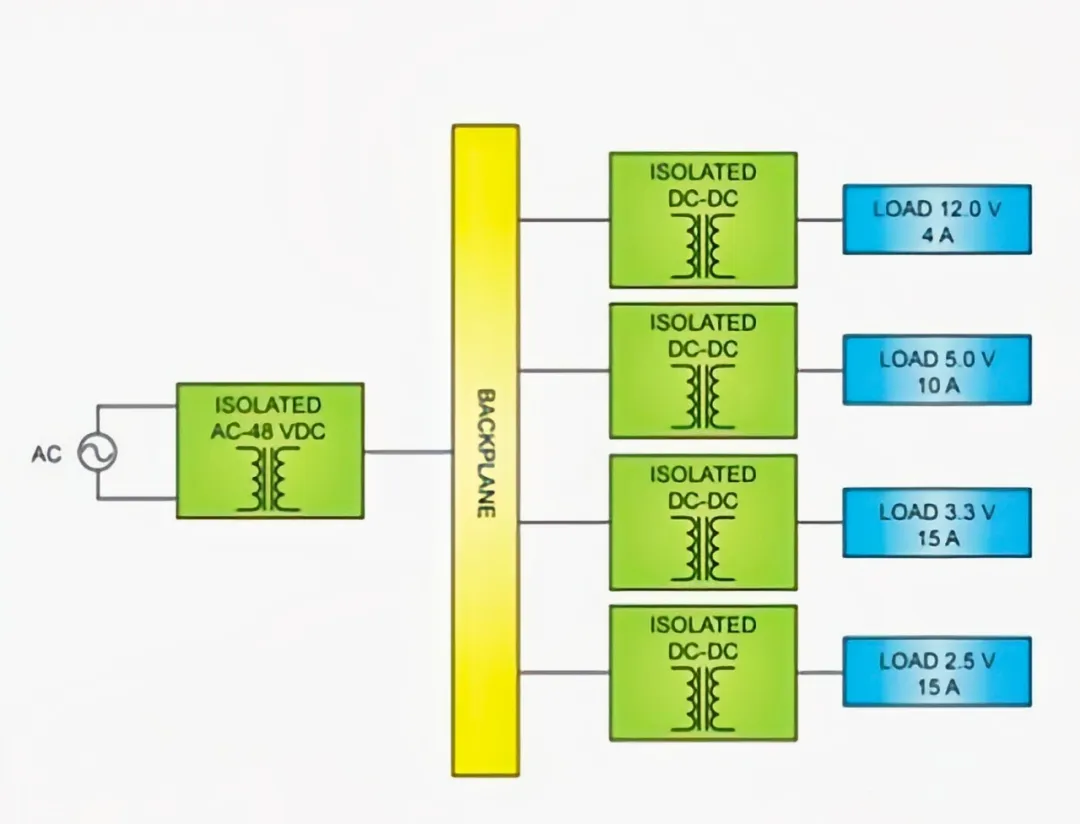
48V Distributed Power Architecture (Image source: Internet)
1.3 Multi-phase buck conversion architecture
It is the specific implementation solution for POL to power extremely high-power loads (such as CPUs/GPUs). By alternately operating multiple parallel synchronous buck circuits to supply power to a single processor, its advantages include: reducing current stress and thermal losses per phase after current division; effectively smoothing output current ripple through multi-phase interleaving operation, reducing reliance on decoupling capacitors; and dynamically enabling/disabling the number of phases based on processor power consumption to optimize light-load efficiency.
1.4 Digital power control architecture
By replacing some analog circuits with digital signal processors (DSPs) or microcontrollers (MCUs), it achieves intelligent power management. It not only enables more complex and flexible control algorithms to optimize dynamic response and energy efficiency but also supports real-time monitoring, parameter adjustments, fault prediction, and remote management (such as based on PMBus/I2C protocols) through software. Advanced designs often adopt a hybrid mode of digital management + analog rapid response, balancing intelligence and speed.
1.5 Modular Power Supply
Widely used in data center-level AI servers. Standardized power modules (such as CRPS) support hot-swap, N+1 redundancy, and online maintenance, ensuring extremely high availability of business operations. Their intelligent functions enable dynamic adjustment of the number of enabled modules based on load conditions, avoiding inefficient operation under light load, and significantly improving the overall energy efficiency of data centers.
2- Challenges Posed to Inductors by the Evolution of AI Server Power Supply Architecture
Innovation in AI server power architecture has imposed more stringent performance requirements on inductors, driving inductor technology to keep pace with power design advancements. Inductor products must meet the following demands.
① Low DC Resistance: The current demands of high-performance AI servers have significantly increased, requiring inductors to possess strong current-carrying capacity and excellent thermal management performance. When inductors carry large currents, they generate heat. Poor heat dissipation can lead to performance degradation or even failure of the inductor material, affecting power supply stability. Therefore, low DC resistance (DCR) design has become a critical parameter for inductors, effectively reducing energy loss and heat rise, enabling the inductor to demonstrate outstanding reliability in high-current applications.
② High Frequency, Low Loss: Modern AI server power supplies demand efficiency levels of 97% or even 99%, with inductor transformers accounting for a significant portion of losses in the system. As power conversion frequencies continue to rise, inductors must balance high-frequency performance with high efficiency, minimizing eddy current and hysteresis losses. The increased losses brought by high-frequency currents necessitate continuous optimization of inductor materials and structures to meet the requirements of a wide frequency range and high efficiency.
③Miniaturization and Thin-profile Design: AI servers have limited internal space, requiring further reduction in inductor size while maintaining performance. Miniaturization and thin-profile design are future trends in inductor development. Through the use of high-density magnetic core materials and advanced molded forming techniques, inductors can be made smaller while also reducing weight, facilitating high-density mounting and effectively saving valuable PCB space. Additionally, these designs must balance mechanical strength and thermal performance to prevent performance degradation in complex environments.
④ High reliability: AI servers typically operate under wide temperature ranges and long-term continuous load conditions. Inductors are required to have good temperature adaptability and reliable stability, capable of effectively resisting the effects of high temperatures and environmental changes to ensure continuous and stable operation of the equipment.
⑤ EMI Performance: The magnetic shielding structure can effectively suppress the damage of electromagnetic interference to nearby components or signal lines, ensuring precise processing of weak signals by the server. High EMI performance inductors can reduce electromagnetic environmental pollution and enhance the overall system's anti-interference capability.
⑥ Low Noise Design: With increasing demands for server noise control, the buzzing sound of inductors has also become a focus. The buzzing noise generated by the vibration of the inductor itself affects the data center environment and user experience. Particularly in large-scale cloud data center server rooms, the importance of low noise design cannot be overlooked. Molded inductor technology and resonance frequency adjustment provide effective solutions for reducing buzzing noise, significantly improving the environmental adaptability of server power supplies.
In summary, inductors face multiple challenges in AI server power systems, including high current, small size, high frequency, strong anti-interference, wide temperature adaptation, and low noise. To meet the stringent application requirements under new trends, continuous progress through material innovation, structural optimization, and process upgrades is necessary.
3- Application and Selection Recommendations for Inductors in AI Server Power Supplies
Inductors in AI server power supplies perform multiple functions such as filtering, chokes, stabilizing voltage and current, and suppressing noise. For the high-performance and high-reliability requirements of AI servers under new trends, selecting the appropriate inductor is crucial. Codaca has focused on high-reliability inductor solutions and has launched multiple high-performance inductor products for AI servers and related intelligent devices, covering various categories such as super high current power inductors, compact high current power inductors, and molded low-inductance high-current inductors.
Among them, the compact high current power inductor CSBA series adopts Codaca self-developed magnetic powder magnetic core material, featuring extremely low core loss, excellent soft saturation current characteristics, and high-frequency low-loss properties. Its slim design saves installation space, making it suitable for high-density mounting requirements. Operating temperature range of -55℃ to +170℃, it can adapt to high-temperature working environments. The CSBA series inductors meet the performance requirements of GaN power supplies for inductors with high-frequency low-loss, high power density, and wide temperature range, and are widely used in core modules such as DC-DC converters and switching regulators.

The molded inductors of the CSHN series, designed specifically for AI applications, adopt a molded structure with ultra-low buzzing noise. They feature ultra-low inductance, extremely low DC resistance, excellent soft saturation characteristics, and high current carrying capacity. The products use a slim design to meet the demands of miniaturization and high-density packaging for AI chips and power modules. The operating temperature range is -40℃ to +125℃, meeting the stringent requirements of intelligent computing devices.
When selecting components, engineers need to consider the load characteristics, current, size, operating frequency, and cooling conditions of the AI server to choose the most suitable inductor model. For example, in compact server chassis with limited space, the CSBA series of compact high current power inductors would be an ideal choice. To meet the requirements of AI applications for low inductance, high current, and small size, the AI molded inductor CSHN series can be selected. Properly matching high-performance inductor products can maximize the power conversion efficiency and system stability of AI servers.