Medical electronic devices support the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of diseases, playing a crucial role in the healthcare field. Due to their involvement in life safety, medical devices impose extremely stringent requirements on power systems, necessitating compliance with rigorous medical safety standards, as well as exceptional reliability, ultra-low noise, compact and robust structures, and outstanding environmental adaptability.
1- Challenges Faced in Medical Electronic Power Design
Since medical devices heavily rely on complex electronic systems, they also encounter various issues common to electronic circuits, such as component losses, electrical noise interference, and environmental stress effects. Additionally, medical devices must address challenges specific to the medical field, such as adhering to strict medical device safety standards, complying with IEC60601 and other medical safety standards, meeting device sterilization requirements, and ensuring high demands for continuous reliability in critical life-threatening applications.
1.1 Electrical Challenges
Integrating power systems into medical devices presents unique electrical challenges that do not exist in general electronic devices. High reliability and continuous availability are crucial, as many medical devices require 24/7 uninterrupted operation and cannot tolerate unexpected downtime, especially in life-support or critical task medical application scenarios. For life-critical applications, backup power is essential, requiring instantaneous switching to batteries or uninterrupted power supplies (UPS) to prevent operational interruptions.
1.2 Mechanical Challenges
To ensure the power design is compact and robust within limited internal space without compromising performance or safety, medical device power systems also face mechanical design challenges. In portable and wearable medical devices, reducing weight is crucial for improving usability, minimizing fatigue, and ensuring patient mobility. Therefore, downsizing the power system is an inevitable trend.
Heat dissipation management is another critical factor to consider, as small enclosures may accumulate heat, which must be safely dissipated without increasing noise, causing component failure risks, or causing discomfort to the patient.
1.3 Environmental Challenges
Power systems in medical devices must operate reliably under various environmental conditions. This includes tolerance to different temperatures and humidity levels, which can affect device performance and component lifespan. For mobile, field-deployed, or emergency-use devices, the ability to withstand vibration, mechanical shock, and operational shock is equally essential to ensure a stable power supply and prevent internal damage.
1.4 Safety Standards
Medical power supplies must comply with international standards such as IEC 60601-1, which specifies general safety and basic performance requirements for medical electrical equipment. It covers many electrical challenges, including isolation, leakage current limitation, and fault tolerance, while also demanding mechanical integrity and environmental durability. Complementary standards like IEC 60601-1-2 address electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements, ensuring reliable operation of the equipment without generating electromagnetic interference (EMI) or being affected by it.
2- Main Applications and Requirements of Inductors in Medical Power Supplies
Inductors play a crucial role in medical electronic devices, with power management being the most fundamental and important application. Their applications mainly include:
2.1 Switching Power Supplies and DC-DC Converters: Inductors are the core components of switching power supplies, working in conjunction with switching transistors and capacitors to store energy, filter signals, and convert voltage. Whether in the main power supply of large imaging equipment (such as CT, MRI) or the battery management circuits of portable devices (such as monitors, infusion pumps), power inductors are indispensable. They efficiently convert alternating current to the various DC voltages required by the device or perform step-up and step-down conversion of DC voltage.
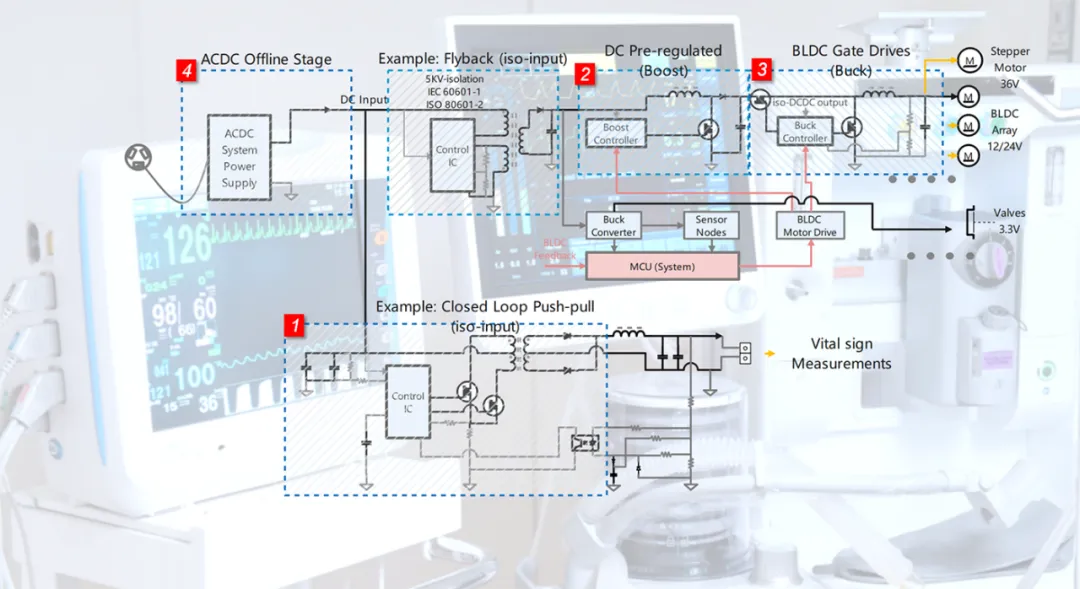
Schematic Diagram of Power Supply Application in Medical Devices
2.2 Noise Filtering and Electromagnetic Compatibility: Medical devices are highly sensitive to electromagnetic interference (EMI), and the noise generated by the devices themselves should not interfere with other equipment. Magnetic beads and common-mode inductors are widely used at the power input end and key circuit nodes to filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring the device meets strict electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards (such as IEC 60601-1-2).
Due to the particularity of the application scenario, inductors used in medical equipment power supplies have higher electrical performance requirements than ordinary consumer-grade inductors. Their demands are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
◾ High reliability: Medical devices are related to life safety and must be ensured to operate stably throughout the device life cycle, requiring an extremely low failure rate.
◾ Low noise: Low noise design to prevent power supply noise from interfering with internal sensitive analog circuits (such as ECG, EEG amplifiers, etc.)
◾ High efficiency: Using low-loss magnetic core materials to reduce inductor loss and heat generation, especially crucial for implantable and portable devices, can extend battery life.
◾ Magnetic shielding structure: Use inductors with magnetic shielding structures to prevent magnetic field leakage of various components in medical devices, avoiding interference with surrounding circuits or equipment.
◾ Compliance with safety standards: Inductors (especially isolation transformers) must comply with medical safety standards, ensuring sufficient creepage distance and electrical clearance.
In summary, inductors are the "heart" and "purifier" of the power supply system in medical devices, responsible for efficient energy conversion while ensuring the purity and safety of the power supply. They are an indispensable core component that meets the high standards and stringent requirements of medical devices.
3- Inductor Solutions for Medical Electronic Power Supplies
As mentioned above, inductors play a crucial role in medical power supply systems and must meet the high requirements of medical power supply equipment. Therefore, when selecting products, factors such as high reliability, low noise, high efficiency, and EMI resistance need to be considered.
As a leading magnetic component supplier in the industry, Codaca has been dedicated to the R&D of magnetic core materials, the design and optimization of coils and inductors for over 24 years. Collaborating closely with medical power supply engineers, Codaca provides high-value products for the medical electronics field and offers technical support to help customers select the right magnetic components. Codaca independently develops and manufactures multiple series of inductors, including high current power inductors, molded inductors, and common mode chokes, which have been widely applied in medical devices and components such as ultrasound detectors, blood analyzers, ventilators, blood pressure monitors, and rehabilitation robots.
